Challenges in Project Management/Coordination and Ways to Overcome Them during Implementation
Abstract
The study background, aim, and questions—which draw attention to the many research areas—are highlighted in the chapter 1. Furthermore, the chapter encompasses the problem statement, research importance, rationale, and dissertation structure. The purpose of the study is to evaluate the difficulties associated with the project management process and to identify appropriate solutions that can be implemented to lessen the difficulties.
A literature review helps the assessment of literary materials accessible on the project coordination difficulty and solutions to address it. Various notions concerning the work of the project coordinator have been evaluated in chapter 2 in order to analyse frequent obstacles and propose appropriate ways to minimise the concerns. The conceptual framework, theoretical application, and literature deficit are all covered in this chapter.
The chosen research techniques, which are used to collect information on the difficulties in project coordination and potential solutions, have been explained and justified in the chapter 3. Secondary qualitative research has been used in the study to identify the problems with project coordination and their remedies.
The chapter 4 presents the results of a thematic analysis technique that was used to evaluate the secondary data sources that were gathered in order to understand the research findings. The discourse has elucidated a connection between the literature review and the results, offering a more comprehensive outlook on the solutions for mitigating project management issues.
In chapter 5, an overall conclusion of the research has been provided along with a link with objectives. It has also highlighted limitations, recommendations, and future research questions. This research can be significant for various small and medium-sized companies to recognise the common project coordination challenges and their mitigation process.
Chapter 1: Introduction
1.1. Introduction
Project management is the process of organising and planning projects while managing available resources adequately. It generally consists of the identification and management of the utilised lifecycle, creating a project management team, and guiding the team members effectively through all phases. AHNAIZN Business Group is one of the renowned market research and branding organisation, which offers small and medium businesses with business solutions in the UK. The project coordinator of the firm is expected to coordinate smaller projects along with collaboration with third parties and to ensure higher consumer satisfaction. This chapter highlights the research background, aim, objectives, and questions, which highlight the research areas. In addition to that, the problem statement, significance of research, rationale, and structure of the dissertation are also included in the chapter.
1.2. Research background
“Project management or PM” is a complex ground that involves various methods and processes to deliver a predetermined goal and project standards. It is a way to organise and control a project to ensure that the project meets its goals. A good PM process plays a crucial role in achieving project success by ensuring that the given tasks are finished and the resources are used widely (Salvador et al. 2021). It also ensures that the project is completed within the deadline and the project stays within the predetermined boundaries. Additionally, in the business world PM is essentially important to maintain open and effective communication with the third party vendors. AHNAIZN Ltd is a UK-based respected company, which provides specialised solutions to businesses, charities, and other government organisations (AHNAIZN, 2023). The company is famously known for its unique service, which helps to meet the requirements of its clients.
The project coordinators play a crucial role in PM for the AHNAIZN’s business operation. The project coordinators of AHNAIZN effectively deliver crucial responsibilities in the various aspects of PM, which allows the company to maintain a sustainable reputation (AHNAIZN, 2023). The primary responsibilities of coordinators of AHNAIZN are maintaining deadlines, carefully evaluating finances, and maintaining a good relationship with clients. The field of PM requires good skills and expertise in various aspects for both project coordinators and their teams (Secundo et al. 2022). The skills and qualities of coordinators and teams include maintaining confidential documents, strong coordination skills, managing clients’ information and effectively communicating with all stakeholders related to the specific project. These skills and expertise have a significant role in PM, which allows the entire team to maintain and deliver a successful project.
Moreover, these qualities are essential for boosting the team’s performance and promoting teamwork, which helps everyone to work towards the same project’s objectives (Friedrich, 2023). The collaboration of good skills and the effectiveness of teams are the key elements for delivering success to the project. However, project management has various challenges, especially in terms of not having effective communication and lack of clarity on project objectives. These problems occur when people barely communicate with each other and do not have a well-defined understanding of the project goals (de Almeida Parizotto et al. 2020). It leads to the project delay and the unnecessary consumption of the organisation’s resources. Mitigating these challenges requires effective strategies and proper implementation of PM operations, which can ensure improving communication and the development of flexible PM methods.
1.3. Research aim and objectives
Aim
The research aims to assess the challenges of the process of project management and to highlight suitable recommendations to reduce the challenges during the implementation process.
Objectives
● To discuss the role of the project coordinator in the process of project management
● To identify the required skills for the project coordinator in PM
● To analyse the common obstacles to project management
●To recommend strategies to suitably address challenges during the implementation process
1.4. Research questions
● What is the role of the project coordinator in the process of project management?
● Which skills are essential for a project coordinator in the PM process?
● What are the common challenges that arise in the project management process?
● How can the emerging challenges be resolved during the implementation process of PM?
1.5. Problem statement
PM has various challenges, which negatively impact the overall project and its outcomes. One of the primary challenges in PM is “scope creep”, which occurs due to the unexpected increase in the project’s needs and goals (Haass and Azizi, 2020). It happens due to the changes in clients’ requests and undefined project objectives. This situation requires investing more resources in the project than the initial project plan. Therefore, it causes a delay in the project, increases cost, and negatively impacts overall project standards (Vaagaasar et al. 2020). Ineffective communication is another primary challenge in the PM, which can be caused by unclear objectives, lack of communication channels, and undefined roles and responsibilities.
These issues can cause misunderstanding among the clients and the organisation, which crucially affects the organisation’s reputation. It also negatively affects the project expectation, which leads to the project failure. Resource allocation is another crucial issue that the project faces, which is caused by the overloaded workforce, insufficient access to the required resources, and lack of skills that team members need to complete the task (Shpeizer, 2019). It leads to missed deadlines and compromising with project standards, which can influence the company’s credibility in terms of project delivery.
1.6. Rationale
Project management involves activities, which aim towards organising and optimising the use of a firm’s resources to proceed with a certain task toward completion. It can consist of an ongoing project or a one-time project and the management of resources generally includes finances, technology, personnel, and intellectual property (Chernogorova et al. 2021). Project coordinators are responsible for managing the schedule, budget, and details of the given projects. They are generally responsible for maintaining effective communication with various departments to keep informed everyone about emerging changes in the plan along with organising meetings, reporting, and updating project managers (Safapour et al. 2022). The study aims to analyse the challenges of the “Project management or PM” process to provide appropriate recommendations for AHNAIZN Business Group to overcome common problems.
There are many academic resources available, which highlight the common challenges of PM and its resolutions. However, the recommendation for lessening the challenges during the implementation of the PM process has not been analysed. Well-known in the UK, AHNAIZN offers advisory services to clients and other businesses (AHNAIZN, 2023). It has between 11 and 50 workers, and it has recently grown into the retail and fashion industries. Understanding the successful tactics for managing projects efficiently in small businesses can be aided by analysing the company’s required skills for project coordinators and recommendations for overcoming challenges (Akbar et al. 2019). Other UK SMEs can prevent challenges of project management and evaluate the recommended strategies to reduce obstacles during the implementation of PM. Hence, conducting a study on problems of project management and recommended strategies can be helpful in overcoming common challenges for SMEs.
1.7. Significance of research
The significance of this research is to understand the way businesses can effectively manage projects and the required necessary skills of coordinators, which can help in addressing challenges. It also helps to identify the challenges that UK-based SMEs face in the PM, which can prevent PM difficulties and provide recommendations regarding the strategies during the initial plan (Hussain et al. 2019). Therefore, conducting research on the PM issue and discussing alternative options to mitigate challenges can help UK-based SMEs to have an effective PM process. Additionally, recommendations can also enhance the existing PM process by introducing new strategies, which can assist SMEs in improving their implementation of the PM process.
1.8. Structure of dissertation
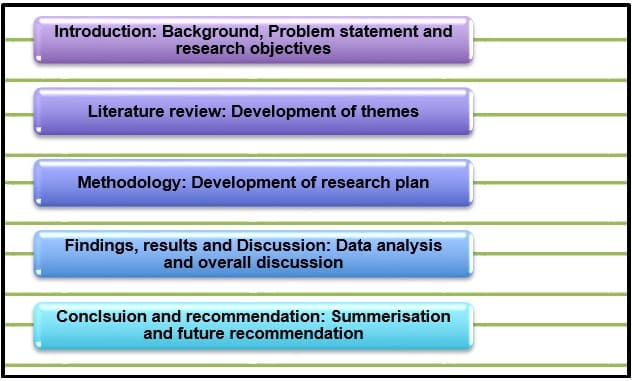
Figure 1: Structure of dissertation
(Source: Self-created)
1.9. Summary
The chapter sheds light on the research areas to outline the challenges of the project management process and to recommend strategies to overcome the obstacles. One of the most well-known business solution companies in the UK, AHNAIZN Ltd. offers public, and commercial organisations practical ways to fulfil their business targets. A successful project depends on a strong project management procedure, which guarantees that all assigned tasks are completed and resources are utilised to the fullest extent possible. AHNAIZN coordinators’ main duties include adhering to deadlines, closely examining finances, and upholding positive client relations. The problem statement has highlighted various challenges of project management such as sudden changes and increase in requirement due to undefined objectives and changes in client requirement. The research aims to provide suitable solutions to tackle the challenges of PM implementation.
Chapter 2: Literature Review
2.1. Introduction
Literature review facilitates assessment of literary sources available on the challenge in project coordination and strategies to overcome them. It has highlighted various concepts regarding the topic, which has fostered a deeper understanding of the existing literature. In this chapter, various concepts regarding the role of the project coordinator have been assessed to analyse the common challenges and have been provided with suitable strategies to mitigate the issues. The project coordinator plays a vital role in managing resources, schedules, and client relationships, which are essential for obtaining the success of the project. The chapter includes the conceptual framework, theoretical application, and literature gap as well.
2.2. Concepts
2.2.1. The role of the project coordinator in the PM process
A project coordinator is a responsible post, which operates the entire project management within an organisation. According to Cunningham and O’Reilly (2019), the coordinator plays various significant roles in project management such as overseeing project management activities, distributing resources, and analysing information. Project coordinators make sure that the project runs smoothly and that the activities of the PM follow every rule and regulation of the organisation. Distributing resources requires coordinators to analyse and understand the project requirements, which allows coordination to understand the requirements of the project. According to Lee et al. (2023), Project coordinators are considered the key players behind the success and failure of the project, which significantly increases their responsibility towards the project. Moreover, the effectiveness of project coordination has the quality to enhance the project outcome.
Critical project tasks are required to break into small and easy parts, which allows the teams to perform them with perfection. As per Saesen et al. (2023), project coordinators work as a facilitators with the primary responsibility to decrease the difficulties that lie in large and complex work. This is a very important role for coordinators, which helps the teams perform their job with full effectiveness and increase the project’s efficiency. Dividing large tasks into small and manageable parts allows the team to understand their role and helps them to increase their accuracy in every level of that task. Tee et al. (2019) stated that the work of a project coordinator makes the project tasks more efficient helping to maintain time and available resources through optimised use. It ensures that every aspect of the project is aligned with its main objectives, which is one of the crucial parts of the project coordinator.
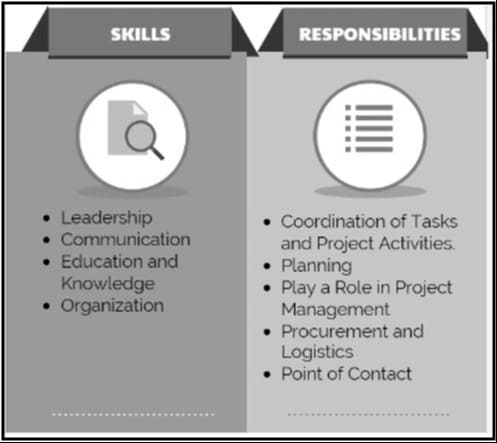
Figure 2.1: Skills and responsibilities of project coordinators
(Source: Cunningham and O’Reilly, 2019)
Working closely with clients is another crucial role of the project coordinator to understand the client’s needs, and objectives, and identify required changes. Martinsuo and Geraldi (2020) stated that project coordinators often find themselves closely engaged with clients, which allows them to understand the client’s needs, demands, and requirements. Therefore, close communication with clients helps to understand in case any requirement for changes are needed. This understanding of the requirements of changes helps them to increase the project efficiency throughout the project lifecycle. As per the understanding of Tee et al. (2019), effective client communication is a crucial element of the PM process, which not only ensures that the project meets the client’s needs but also exceeds them to enhance the client’s experience. This helps project coordinators to increase their skills in deep understanding of PM and interpersonal skills.
Proper allocation of tasks by the project coordinator based on the quality and expertise of the internal team can ensure that the project meets clients’ demands. Cunningham and O’Reilly (2019) opined that task allocation within the PM process is a crucial project coordinator’s responsibility. Enhancing project efficiency requires task allocation based on the team’s skills and expertise, which is the only way to increase the effectiveness of outcomes. Often clients’ additional demands can be fulfilled by the skills and expertise of the team without spending further resources of the organisation. Saesen et al. (2023) stated that the project coordinator leads the team to maximise their skills, resulting in higher productivity. Project coordinators need to be aware of the skills and expertise of the team, which enables them to make wise decisions.
As per the understanding of Lee et al. (2023) analysing risk and opportunities is another crucial responsibility of project coordinators, which allows the project to run with perfection and effectiveness. Moreover, establishing oneself as a central point of communication to connect with all project individuals of another important role of coordinators. The project coordinator plays a vital role in collaborating with the commercial and pre-sale teams to deliver small projects, maintain cost, and schedule as well.
2.2.2. Essential skills for project coordinator in the PM process
PM is a critical and extensive task, which requires various skills and expertise to perform. Workineh (2022) stated that it requires a significant amount of experience in a similar field, which can allow one to perform and understand responsibilities without any confusion. Establishing oneself as an effective project coordinator requires having a strong background in a field that is relevant to the PM. Managing a team requires effective necessary knowledge and experience, which can project coordinators guide their teams. Ngo and Hwang (2022) stated that having experience related to the PM process provides the knowledge and insights required to effectively deal with complications that lie in the management process. Therefore, possessing experience allows project coordinators to make informed decisions and deal with challenges.
One of the primary responsibilities of project coordination is to communicate with all the stakeholders of the projects, which requires having good communication skills that can establish effective communication. As per the understanding of Fioravanti et al. (2020), a project involves various stakeholders and every individual has a specific contribution to the project’s success and failure. Therefore, an effective communication function can allow project coordinators to maintain a balance of passing information, which can provide sustainable progress to the project. According to Taneja (2022), the importance of having excellent communication abilities ensures that the information is accurate and communicates effectively to the individuals related to the project. Furthermore, effective communication builds collaboration, minimises misunderstandings, and engages all stakeholders, which plays a crucial role in decreasing confusion in the PM process.
Project coordinators are also considered leaders or captains of the entire PM process, as they are the responsible persons for making and maintaining decisions. According to Fioravanti et al. (2020), the PM also requires organisational skills such as managing project documentation and resources. These organisational skills are crucial elements for creating and maintaining order through the project lifecycle. Maintaining documents allows important insights, which shows the project’s progress and effectiveness. Project resources are the fundamental elements that hold the project and influence the project’s success and failure. Peña and Muñoz (2020) stated that effectively managing the project resources not only decreases the project cost but also enhances the project’s efficiency. Hence, organisational skills such as maintaining documentation and resources increase the quality of a project’s coordinator.
Project coordinators are also required to know visual representations such as flowcharts, which allow the individuals to deliver their plans to their fellow workers. As per the understanding of Taneja (2022), an effective project coordinator is required to have the ability to express difficult project plans and ideas with flowcharts, diagrams, and Gantt charts. The representation through visual information allows all stakeholders to get the overall idea regarding project goals, requirements of resources, and lifecycle. According to Ngo and Hwang (2022), team members’ performance can be tracked through visual data, which not only helps management to identify low performance but allows individuals to work on the gap. Therefore, visual representation helps organisations identify bottlenecks and spend resources to enhance the project’s progress.
Time management skills are also important considering following and managing project schedules. As per Peña and Muñoz (2020), the importance of completing a project within the planned timeframe shows the competency of the project coordinator. Time management also helps coordinators reduce the waste of resources that are often consumed by extending project timeframes. Moreover, knowing the tools of PM such as “Basecamp” or “Trello” can provide another advantage ground for project coordinators. Leadership is another crucial role competency for project coordinators, as they are required to communicate with various teams and employees to ensure a suitable project. Workineh (2022) stated that appropriate leadership skills are essential for guiding the employees through the PM process and any changes that can emerge due to the recognition of inefficiencies in the process. Ngo and Hwang (2022) opined that adequate leadership skills assist project coordinators in facilitating effective communication with employees. Furthermore, attention to detail, adequate documentation skills, and organising abilities are also required for project coordination.
2.2.3. Assessment of common challenges of project management
The lack of communication channels plays a significant role in developing challenges in the PM process, which not only affect the overall project effectiveness but also the client’s expectations. As per the understanding of Kabeyi (2020), ineffective communication can produce various challenges within the PM such as improper task distribution, unclear instructions, undefined roles, and unclear goals. Ineffective communication causes improper task distribution due to the lack of information regarding team credibility. Keegan and Den Hartog (2019) stated that ineffective communication also causes difficulties in understanding instruction and roles, which increases difficulties and confusion for team members. Lack of communication develops challenges such as project inefficiency, duplication of efforts, and frustration among team members, which affect project objectives.
The lack of a clear project goal also affects the business objectives, which is another crucial challenge in PM. According to Haass and Azizi (2020), unclear project goals increase confusion among the workforce due to insufficient planning, which negatively affects the overall business objectives. As any project’s success depends on its goals and objectives, therefore, not having proper communication among team members causes delivery of insufficient efforts. Poor communication develops confusion regarding project goals, which leads team members to problems working together. Khan et al. (2022) stated that accountability is very important for the PM process, where every individual has a different responsibility and does not perform or meet that accountability that individual. The lack of accountability can affect every step of the PM process, which eventually decreases the effectiveness of the project.
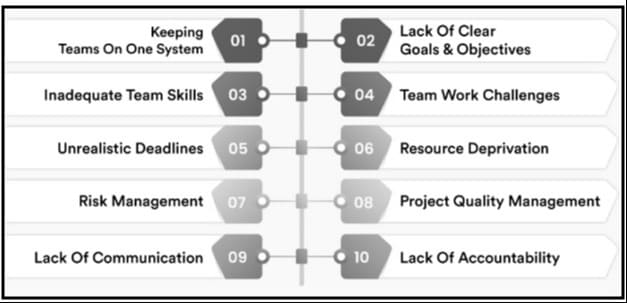
Figure 2.2: Challenges of project management
(Source: Stonehouse and Konina, 2020)
Project coordinators often face issues such as keeping team members on the system due to the various objectives and tasks. As per the understanding of Stonehouse and Konina (2020), various tasks require different approaches to perform and lead team members to get confused and pressured. Another challenge that influences PM efficiency is inadequate team skills. PM involves various tasks, which require different skills and expertise. A team can be assigned to any task but its credibility depends on the individuals in the team and their skills, therefore insufficient skills not only hamper the project’s effectiveness but also decrease the team’s confidence. As per Kabeyi (2020), effective team skill and expertise helps project coordinators to deliver a successful project. It also helps the team’s other members gain knowledge from each other and increase their effectiveness.
Despite having essential skills in employees and opportunities, a project can fail due to its deadline. Project deadlines are not only made to meet clients’ needs but are also recognised as performance parameters. According to Haass and Azizi (2020), an unrealistic deadline severely affects various factors of PM such as project success rate, team members’ confidence, and increased mental pressure. Unrealistic deadlines increase the pressure on team members to complete the project, which decreases outcome efficiency and makes it impossible. As per the understanding of Stonehouse and Konina (2020), increased pressure on task completion leads to employee dissatisfaction and project inefficiency. It also plays a crucial role in redirecting the entire project to failure. Teamwork is another challenge caused by the lack of individual collaboration that influences the outcomes of the PM process.
Minimising project costs also develops issues such as resource deprivation. According to Khan et al. (2022), it plays a crucial role in decreasing the project’s effectiveness and leading to the compromise of project quality. In addition, insufficient resources create problems for the team to provide their best, which affects the overall project quality management process.
2.2.4. Suitable mitigation strategies for a smoother PM implementation process
Communication problems in PM can be solved through regular meetings, which can provide updates and reviews regarding individuals’ performance and project progress. Senabre et al. (2019) opined that organisations could invest in developing communication tools that connect all individuals connected with projects. Developing project management software and collaboration tools can help mitigate communication challenges in PM. Furthermore, training programs and workshops can be arranged, which can help to enhance the team’s communication skills. Tereso et al. (2019) stated that training programs for improving communication skills require being on enhancing active listening and conveying instructions clearly, which can help the team to understand the significance of training. Moreover, creating a verbal communication culture can also decrease challenges in the PM process.
Utilising the SMART criteria can ensure the project’s “specific”, “measurable”, “achievable”, “relevant”, and “time-bound” goals. As per the understanding of Puška et al. (2020), implementation of a KPI system can ensure that every individual is following its instructions by tracking their performance, which can help to increase accountability within the PM process. Developing a communication plan at the start of the project initiation stages can help to avoid challenges regarding communication. The plan needs to outline the process of how the information can be disseminated and who is responsible for gathering and providing updates. Mishra (2020) stated that having an effective communication plan can ensure that all the stakeholders are on the same system. It also helps to increase the efficiency of implementing other strategies through communication.
Addressing the issue of affecting clients’ expectations due to various challenges required the involvement of clients within the project planning and decision-making process. Moradi and Shadrokh (2019) opined that regular meetings, status updates, and reviews could allow various stakeholders to stay updated regarding project changes and progress. Team members are required to be encouraged to share regular updates on given tasks, which not only builds communication but also allows clients to stay updated on the project. According to Senabre et al. (2019), “project management software” and “collaboration tools” play a crucial role in increasing project efficiency. These tools play a vital role in communication, task tracking, and document sharing. It allows project coordinators to monitor and make sure that the team’s effectiveness is properly utilised by this “project management software”.
During the implementation of PM, it is required that the team get clear roles and responsibilities. Puška et al. (2020) state that clear and specific roles and responsibilities need to be set from the outset. In addition, by utilisation of SMART criteria, project coordinators can also make sure that the roles and responsibilities are well distributed. Minimising the issue regarding planning and documentation project coordination needs a comprehensive project plan and task lists. Tereso et al. (2019) stated that accountability is one of the primary element of PM, which ensure that all the involved individuals are performing at their best. Therefore, implementing an accountability framework can play a crucial role in addressing challenges in the PM process. This framework can help in distributing adequate responsibility to the individual, who has been assigned specific tasks.
Unrealistic deadlines need to be addressed with a realistic and data-driven approach. Project coordinators need to conduct an assessment, which can help set realistic deadlines. According to Moradi and Shadrokh (2019), Promoting a culture of team collaboration and building a team with balanced skills and experiences can solve issues regarding teamwork challenges and enhance team skills. Proper resource allocation at the project’s initial stage can minimise resource deprivation issues.
2.3. Conceptual framework
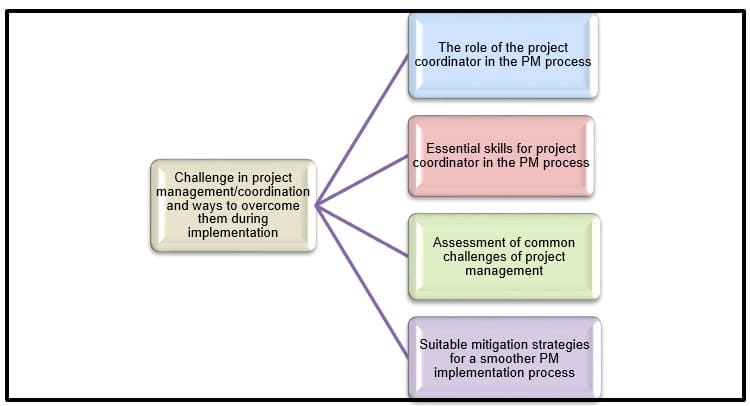
Figure 2.3: Conceptual framework
(Source: Self-created)
2.4. Theoretical application
Scientific management theory
The “Scientific Management theory” is a process of improving the efficiency of the workforce through assessing the work process with the scientific method. The scientific method usually consists of three distinct stages; observation, experimentation, and analysis (Taylor, 2023). This theory is generally used by businesses to observe their workplace, test various processes of efficiently completing tasks, and assess the impact of changes. This framework relies on four basic principles such as choosing a science-based method, selecting workers based on their skills, continuous performance monitoring, and appropriate division of workload (Giglioni and Bedeian, 2019). The primary goal of scientific management is to increase efficiency by decreasing the time required for various tasks and generating higher profits.

Figure 2.4: Scientific Management Theory
(Source: Taylor, 2023)
In the case of proper implementation, this framework helps to improve overall productivity. The managers can observe the work process to identify the gaps to implement appropriate strategies to improve outcomes (Kamal, 2020). The selection process of the workers for a specific project is generally based on their skills and experience, which contributes to the quality of the work. Additionally, managers continuously monitor employee performances and enable adequate work distributions. As a result, this framework depends on reliability and efficiency along with setting clear expectations from the employees. The application of this theory can help in resolving the challenges of project management (Giglioni and Bedeian, 2019). The challenge of task distribution can be resolved through appropriate workload distribution, which can be achieved by following the principles of scientific management. Additionally, it can help in providing the employees with clear goals, which can help in achieving higher outcomes in projects.
2.5. Literature gap
The study has highlighted various concepts by analysing the existing literary sources related to project coordinator and their role in project management. It has assisted in identifying common challenges of the project management process and their probable solutions. However, a significant gap can be identified as it has not been analysed the impact of advanced technology on mitigating the common challenges. Advanced technology has revolutionised the business industry with its higher efficiency and speed along with its ability to detect anomalies (Vrontis et al. 2022). Therefore, this gap can be addressed in the research, which can provide a comprehensive understanding of probable mitigation strategies available to the project coordinator for the PM process.
2.6. Conclusion
The chapter has shed light on the various concepts related to project coordinators. The project coordinator’s proper work allocation based on the quality and competence of the internal team helps ensure that the project satisfies the demands of the clients. The project coordinator is critical in coordinating with the commercial and pre-sale teams to deliver modest projects on time and under budget. Various skills required for the project coordinator such as communication, adequate knowledge of the project management process, and experience have been highlighted. Challenges such as maintaining a budget, proper communication, and schedule, can be addressed through creating open communication channels and utilisation of SMART objectives.
Chapter 3: Methodology
3.1. Introduction
Research Methodology provides in-depth information about the carrying out process of the research. It provides a detailed approach to the research to ensure valid and reliable results to address the research aim and objectives. It highlights the type of data being collected, data sources, and way of data analysis for the research. Methodology provides a comprehensive view of approaches and methods, which are used to reach conclusions in a research. In this chapter, the chosen research methods have been described and justified, which are used to gather data regarding the challenges of project coordination and their probable solutions. In addition to that, it has highlighted selected philosophy, approach, design, choices, data collection, and analysis.
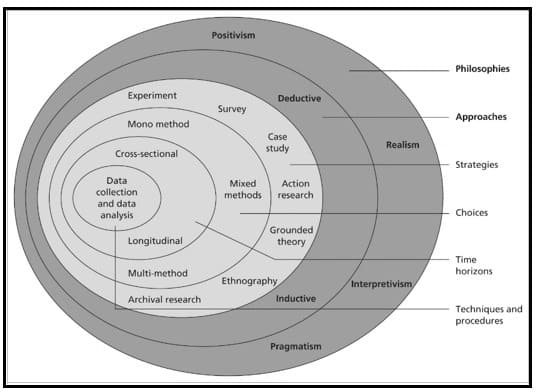
Figure 3.1: Research onion
(Source: Iovino and Tsitsianis, 2020)
3.2. Research Philosophy
Research philosophy can be regarded as a belief system, which highlights a suitable process of collecting data regarding a certain phenomenon for research. It is usually aligned with the collection of proper knowledge and the determining appropriate data sources, which is interconnected with the nature of the study (Snyder, 2019). Research philosophy generally ensures the integration of suitable data collection and assessment processes for the study. Research philosophy can be grouped into three main categories; positivism, interpretivism, and realism. Positivism generally relies on factual knowledge to gain adequate insight regarding a certain event. Furthermore, the application of positivism in research generally needs a large set of data and aids in gaining an objective viewpoint regarding an event (Newman and Gough, 2020). On the other hand, realism depends on scientific assumptions to gain knowledge about a certain phenomenon. However, one of the major disadvantages of realism is it does not consider individual perspective.
On the contrary, interpretivism assists in assessing a phenomenon considering the value system of society and provides an in-depth understanding. In this research, interpretivism has been selected as the research philosophy to analyse the challenges of project coordination. The application of interpretivism generally requires a small set of data, which increases efficiency in the data collection process (Al-Ababneh, 2020). One of the major advantages of interpretivism is its ability to comprehend the distinction between humans and their behaviour despite the common social structure. In this research, interpretivism has assisted in producing data with high validity and focused on personal motivations and meanings (Newman and Gough, 2020). As a result, it has helped in analysing various perspectives regarding the challenges in project coordination and provided a wide range of solutions to resolve the issues. Interpretivism has assisted in considering the social context and interpersonal dynamics in detail to deliver a comprehensive understanding of the challenges of project management.
3.3. Research Approach
The way research is conducted and allows it to collect and analyse data systemically is known as the research approach. The research approach has three different segments, which are “inductive”, “deductive”, and “abductive” approaches (Greening, 2019). The abductive approach allows researchers to study situations that have not been understood yet. On the other hand, the deductive approach plays a crucial role in identifying whether the selected ideas in the research are reliable or not. The inductive approach has been selected for this study, which is expected to identify the challenges that lie in project management and their appropriate solutions (Dodds and Hess, 2020). Additionally, the inductive approach is especially known for its effectiveness in collecting data and analysing situations when there is very little information available regarding the study.
The inductive approach primarily has three stages, which are known as observation, identifying patterns, and building a theory. The observation stage generally gathers information regarding the study, which helps to conduct the study further through an inductive approach. Identifying patterns is the stage where the collected data are analysed and allows the researcher to identify the common pattern in the situation (Budianto, 2020). The last stage where the theory is developed based on gathering data and identifying patterns, which helps to build an understandable research theory. As a result, it is expected that the inductive approach can be useful in terms of analysing the challenges in project management and identifying their remedies.
The inductive approach has various advantages, where it allows the researcher to be flexible and able to make a complete point of view. The flexibility allows the researcher to modify the research topic based on available data (Budianto, 2020). The approach allows the researcher to look at all available data rather than just focusing on the developed theory, which helps the researcher to have a complete view of the research.
3.4. Research design
The research design is the way of conducting research, which helps the researcher to identify what is required to be achieved and how the root map can be designed. In simpler terms, the research design is a scientific framework, which helps the researcher to identify techniques and ideas for the specific research (Delios et al. 2023). It helps the research to develop and continue on the root map, which can allow the research to reach its conclusion. The research design has five different types of design such as “experimental”, “correlational”, “diagnostic”, “explanatory”, and “descriptive”, which allows to conduct of research. The experimental is a common type of design, which helps researchers to examine the variables of the research and the way they intersect with each other.
This research design allows the researchers to manipulate a single variable, which further helps them understand how the changes in that variable influence others. On the other hand, the correlational design promotes observation of the relationship between multiple variables without manipulating their cause and root (Dzwigol, 2022). It allows researchers to understand how multiple variables are associated and react in the real world with each other. The diagnostic design is significantly helpful for identifying the root cause and generating solutions based on the issue. The research design incorporates various approaches such as marketing to identify the areas that require development and have potential growth qualities (Babii, 2020). The explanatory design type is significantly helpful in terms of the lesser availability of information. The design type helps to understand why a specific situation or complication occurs with limited data.
The explanatory design focuses on questions such as why and how an event took place. However, descriptive research has been designed to conduct a systematic process of examining and describing the subject’s behaviour without manipulating it. The descriptive design is significantly important as it allows surveys, polls, observation, interviews, and case studies to analyse a situation (Delios et al. 2023). Following descriptive methods allows the researcher to have an in-depth understanding of the phenomenon by questioning the situation. The descriptive design has been selected for this study, which is expected to highlight the challenges in project management and possible solutions. The primary advantage of this design is it allows the collection of data and information from a wide range of sources (Babii, 2020). It can provide various insights regarding the challenges in PM, therefore, the solution can be identified properly. Descriptive allows different aspects of a topic to be explored, which can provide a better understanding of PM.
3.5. Research Strategies
Research strategies are the plans or schemes, which help in proceeding with the activity of finding, collecting, and assessing the information regarding an event. It usually has a higher influence on the data collection process of the research selected based on the available time of the study, aim, and objectives (Ryder et al. 2022). It is divided into seven diverse categories; case study, survey, experiment, grounded theory, action research, archival research, and grounded theory. The experiment utilises an empirical method to conduct detailed research; whereas surveys have the ability to generate a large amount of data regarding an event. However, in the experiment, subjects or the chosen phenomenon are investigated and tested in a controlled environment to examine the impact of various elements on each other (Zawacki-Richter et al. 2020). Action research facilitates systematic research, which aims to resolve common challenges by finding efficient solutions.
It considers the complex intricacies of society to resolve the challenges, which emerge in specific conditions. On the other hand, a case study is one of the most common methods of research in industrial marketing, which analyses various available case studies related to a certain event (Sileyew, 2019). Grounded theory relies on qualitative methods, which facilitates the development of theory relying on systematic data acquirement and assessment. In addition to that, ethnography refers to the complex social research conducted through various processes such as interviews, observations, and more. Archival research uses journals, articles, and historical archives to determine the gap in the existing research (Urcia, 2021). In this research, the case study has been selected as the research strategy for identifying the challenges of project coordination.
It has assisted in examining various challenges, which occur in the process of project management and analysing their probable solutions. The case study approach has helped in gathering a wide range of information regarding the project management process, which has assisted in gaining broad and comprehensive insight regarding the probable solutions to the project coordination process.
3.6. Research Choices
Research choices inform the types of data being used in the research process. Research choices are generally of three types; mono, mixed, and multi-method. The type of research choice selected for a study has a significant impact on the process of data collection and analysis procedures (Patel and Patel, 2019). It relies on the type of data, such as qualitative and quantitative information required to be collected for the study. The mono method highlights the use of only a single type of data such as qualitative or quantitative for a specific research. The mixed method highlights the process of using both qualitative and quantitative to gain an in-depth understanding of the research topic.
On the other hand, multi-methods generally use more than two methods to gather relevant information regarding research. For instance, the use of thematic and content analysis in addition to quantitative data gathering is an example of multi-method research (Ocaña-Fernández and Fuster-Guillén, 2021). Due to the use of only one type of data collection mono method requires less time compared to multi and mixed processes. In this study, the mono method has been selected to acquire only qualitative information regarding the problems of project management. It has assisted in decreasing the required time for data collection and the analysis process (Zawacki-Richter et al. 2020). It has aided in collecting a specific type of data regarding the project management process, which has simplified the data assessment process as well.
3.7. Time Horizon
Time horizon highlights the timeline for research, which generally informs the time and frequency of data collection regarding a certain topic or event. The time horizon determines the frequency of data collection at various points in time during the research. There are mainly two types of time horizons; longitudinal and cross-sectional (Chivanga and Monyai, 2021). Longitudinal studies allow the researchers to collect data at various points in time, which helps them compare the changes and identify new patterns. As a result, the longitudinal process generally extends the data collection process as information is collected multiple times (Willmott, 2020). On the other hand, cross-section studies require the gathering of relevant information only one time. Hence, it requires comparatively less time than the longitudinal process.
In this research, a cross-section approach has been chosen to conduct the research on analysing the challenges of the project coordination process. It has assisted in the faster collection of relevant data regarding the research, which has increased the efficiency of the data collection process. Hence, the cross-sectional approach has aided in reducing the period for data gathering.
3.8. Sampling Techniques
The sampling techniques refer to the process of collecting data from a specific group of individuals within a larger population. The sampling methods can be segmented into two types such as “non-probability sampling” and “probability sampling”. The “non-probability sampling” refers to the collecting information method, where the samples are collected from a non-random criteria base (Djafar et al. 2021). This sampling method is easier and cheaper, which makes it risky in terms of sampling bias. On the other hand, the probability sampling method allows every individual to participate in the information-collecting process, which allows a researcher to get vast information regarding a specific event (Sileyew, 2019). Probability sampling is primarily used in “quantitative research”, which makes it significantly helpful in the context of collecting data from a larger population.
The probability method can be divided into four types of sampling such as cluster sampling, systematic, stratified, and simple random. Cluster sampling represents the process of collecting information by dividing a large population into subgroups. Systematic sampling refers to the process of assigning individuals with specific numbers, which allows the sampling method to collect information from individuals at regular intervals (Tayebi Abolhasani, 2019). Stratified sampling plays a significant role in dividing a large population into subpopulations, which helps researchers ensure that the data of subpopulations are properly represented in the sample. The simple random method has been selected in this research to identify the challenges in PM and their possible remedies. A simple random sampling method allows every individual of the population to be selected. This sampling method includes the entire population in the data collection process without focusing on a specific group of samples.
3.9. Data collection
Data collection is a process of collecting information regarding a certain event or research topic. Based on the process of collection, data collection is of two types; primary and secondary. In the primary process, relevant information regarding the research is generally collected through interacting with participants through surveys, interviews, and polls (Marx, 2023). On the other hand, the secondary process utilises data from the existing research by gathering journals, articles, and prior research papers. In contrast to the primary process, secondary data collection requires less time. Additionally, based on data type, the data collection process can be further divided into two groups; qualitative and quantitative (Urcia, 2021). Qualitative data is generally descriptive in nature and can be acquired through conducting interviews or collecting information from secondary sources.
On the other hand, quantitative information is collected by conducting surveys, polls, and collecting statistical information from various sources (Ocaña-Fernández and Fuster-Guillén, 2021). This research has employed a secondary qualitative process to collect information regarding the challenges of project management and their probable solutions. Authentic sources such as Google Scholar and ProQuest have been used to gather journals, articles, and research papers regarding the project management process. The secondary quantitative data is informative in nature, which has assisted in determining various patterns in the collected data sets to ensure recognition of appropriate mitigation strategies for challenges of project coordination.
3.10. Data analysis
Data analysis refers to the procedure of assessing and examining the collected data to answer the research questions. Data analysis is of two types; primary and secondary (Chivanga and Monyai, 2021). As the research used secondary sources for data collection, thematic analysis has been used to analyse the collected information on the challenges of project coordination. The thematic analysis process has provided a higher flexibility of study and has highlighted various patterns related to the problems of project management.
3.11. Inclusion and exclusion criteria
The “inclusion and exclusion criteria” highlight the factors, which are maintained during the data collection process. In this research, older literature sources, which have been published before 2019 have been excluded. Additionally, sources, which are available in languages other than English are also excluded from the study. On the other hand, the inclusion criteria for the research are sources, which are available in English and published between 2019 to 2023.
3.12. Ethical considerations
Ethical considerations are an essential part of research, which helps in maintaining ethical guidelines. Plagiarism has been strictly avoided in the study and the collected research sources have been accurately cited. The data protection law has been maintained in the research to provide credible research outcomes (KANG and Hwang, 2021). Moreover, in order to collect authentic and credible data for the research, sources such as Google Scholar and Proquest have been used. It has helped in gathering relevant and authentic information regarding challenges faced in the project coordination process. Additionally, the collected data has been stored in a “password-protected folder” to ensure data security.
3.13. Conclusion
The chapter has shed light on a comprehensive planning of the research process. The research on identifying the challenges of project coordination and their solutions has been conducted with the application of secondary qualitative research. It has used existing journals, articles, government publications, prior research, and online sources to gather credible information for the research. Moreover, older sources prior to 2019 and sources, which are not available in English, have been excluded from the study. The research has been conducted by maintaining appropriate data protection regulations and ethics to ensure proper research outcomes.
Chapter 4: Findings and Discussion
4.1. Introduction
Project coordination is the process of daily management of various tasks within projects. Project coordinators are responsible for streamlining workflow and managing deadlines for various tasks. They also facilitate daily communication with clients to reduce risks and acquire positive project outcomes. In this chapter, a thematic analysis process to highlight a few themes to comprehend the findings of the research has assessed the collected secondary data sources. The discussion has established a link between the literature review and the findings to present a broader perspective on the mitigation strategies for overcoming the challenges of project management.
4.2. Thematic Analysis of Findings
4.2.1. Theme1: Importance of Client Involvement and Expectation Management in Project Management
The role of project coordinator goes beyond the responsibility of just managing various tasks associated with a project. Project coordinators are responsible for establishing a strong connection with clients and ensuring their interests and expectation is understood. As a result, project coordinators need to collaborate with the clients in the PM process to determine their specific needs to ensure their expectations are matched (Bahadorestani et al. 2020). It highlights the importance of daily meetings, reviews, status updates, and the utilisation of project management tools. These activities inform the vital role of clear communication in the PM process as it enable the project coordinator to manage and address the expectations of clients. Effective project coordination signifies the ability of the project coordinator to efficiently collaborate with clients. It assists project coordinators in building a strong relationship along with comprehension of the aim of the project.
Constant communication with the clients is essential to project success, which facilitates an appropriate understanding of the demands and requirements of clients. Project coordinators are responsible for managing ongoing communication with the clients to understand their vision regarding projects (Larsson and Larsson, 2020). It can help in acquiring higher satisfaction among the clients as effective communication can help in recognising the specific changes in demands and requirements. Project coordinators collaborate with the clients to understand their vision, ideas, and true purpose of the project, which underscores requirements (Lehtinen and Aaltonen, 2020). Effective project coordination affects the outcome of the projects, which enables companies to meet the requirements of the clients precisely. It highlights the crucial role of close communication between project coordinators and clients.
Expectation management is an integral part of the PM process, which emphasises the role of the project coordinator. Project coordinators generally conduct daily meetings to update the clients on project progress and direction, which assist them in ensuring the correct integration of clients’ visions into the project process (Abou-Shouk and Soliman, 2021). Managing effective relationships with the clients facilitates swift identification of necessary changes. It helps the project coordinators in keeping the project on track to obtain positive outcomes. Moreover, the utilisation of various software and management tools has become effective in the PM process in streamlining the whole process, which enables in provision of real-time data to the clients (Tran et al. 2022). Therefore, adequate client management is an essential factor in PM in which the project coordinator plays a vital role leading to the achievement of project objectives.
4.2.2. Theme 2: Assessment of factors that contribute to efficiency in project management
Project management refers to the process of organising and planning a project to make a successful project delivery. A project coordinator plays a significant role in the successful project delivery process. Project coordination possesses various skills and expertise on different grounds, which allows the project coordinator to increase team efficiency and achieve project goals (Mikkelsen et al. 2020). Experience is the most valuable element in the organisation field, which allows a person to effectively work on the ground. A coordinator with a significant amount of experience is able to analyse the issue in the project and plan mitigating problems accordingly. Relevant experience within a similar field allows the project coordinator to understand the needs, requirements of changes, and proper resource allocation in the project (Farashah et al. 2019). PM involves various tasks such as analysing, planning, managing, and making decisions, which require different training in terms of enhancing knowledge to perform the tasks.
Training provides crucial insights and knowledge regarding the PM, allowing a coordinator to make essential decisions and change the existing process. A coordinator is also required to have organisational skills such as flowcharts and diagrams, which not only allow the coordinator to understand the project dimension but also the team following that coordinator (Derakhshan et al. 2019). An in-depth analysis of skills allows one to understand the significance of communication skills, which allows project coordinators to establish effective communication between the project team and external stakeholders. Clear communication allows the workforce to understand the project objectives, goals, and expectations, which not only reduces confusion in the system but also increases efficiency in the PM (Alvarenga et al. 2019). A transparent communication channel helps to build strong team collaboration and encourages the workforce to align themself with the project objectives.
Conflict resolution is another significant responsibility of the project coordinator, which can be done by establishing a clear communication channel that allows workers to provide their perspectives. Similarly, risk management is another crucial component of project management, which allows coordinators to increase the efficiency and success rate of a project (Farashah et al. 2019). It involves identifying potential risks, assessing the impact of identified risks, risk mitigation planning, monitoring and implementing the planning, and eventually learning lessons from the occurred risk. Monitoring and reporting about the project status, certain changes, and requirement is another crucial aspect of PM, which contribute to the success of the project (Henkel et al. 2019). Coordinators are responsible for monitoring the project’s progress and ongoing activities, which allows them to ensure that the project is on schedule.
The responsible person also sets a “key performance indicator”, which tracks every small detail and progress related to the project management. It allows the coordinator to identify the achievement that the team is achieving throughout the entire project and the areas that require essential changes or development (Alvarenga et al. 2019). In terms of measurement of the project standards and quality, coordinators play a significant role in the initial stages of PM. The initial stage involved coordination with various stakeholders and clients to ensure their expectations were either met or exceeded.
4.2.3. Theme 3: Impact of experience and adequate training in successful project management
Experience and adequate training programs play an essential role in increasing the effectiveness of project coordinators, which results in a successful project delivery. Experience plays a significant role for project coordinators in terms of the decision-making process. where they use previous experience to make effective decisions (Rusakova et al. 2020). The experience of various projects allows them to identify existing potential risks and the possibility of future problems. Addressing this issue increases the effectiveness of the coordinator role and contributes to the success of the project. Due to having various experiences with previously completed projects, project coordinators are also aware of different problems and their solutions (Stanitsas et al. 2021). It helps them to mitigate problems in the current project by following the previous mitigation process.
Experience also aids project coordinators in designing new mitigation plans based on previous experience, which allows for addressing new challenges. Building and maintaining a positive relationship with stakeholders often requires previous experience in handling these project elements (Armenia et al. 2019). The understanding of stakeholders’ engagement and contribution to project management can be crucially important for coordinators. In terms of having working experience with different stakeholders allows the coordinator to understand their requirements and perspectives, which helps to properly align stakeholders with the project and leads to success (Khosravi et al. 2020). The leadership quality of a person allows one to effectively handle a team, which leads the operation to success. Previous experience in leadership in project management significantly helps coordinators arrange and handle people associated with the project, which contributes to the success of the PM.
Similarly, training refers to the methods of gaining knowledge and skills of a process, in terms of PM, it helps to enhance overall efficiency and lead to success. Formal training and exercise allow project coordinators to gain knowledge regarding methodologies of project management (Perez-Encinas et al. 2021). It also educates employees regarding the best practices within the industry, which not only helps to avoid mistakes but also enhances the effectiveness of coordinators. Training programs are also used to educate coordinator about the tools and software related to PM, which increase their knowledge about the utilisation of tools and help in achieving success in the project (Stanitsas et al. 2021). Project management is an ever-changing ground, which requires updated knowledge and expertise.
Therefore, the training programs play a crucial role in providing new information regarding trends, tools, and challenges of the industry, which helps them to tackle situations. Hence, it can be considered that training allows continuous learning opportunities, which not only positively affect the coordinators but also the project’s success (Rusakova et al. 2020). Training is a wide ground, which also focuses on enhancing soft skills such as communication, leadership, and conflict resolution. These soft skills allow coordinators to engage with stakeholders effectively and help them to align with the project goals and objectives. The project coordinators can also take training to enhance their capabilities to address problems, increase emotional intelligence and develop risk management strategies (Khosravi et al. 2020). Throughout the utilisation of advanced risk management strategies, coordinators can identify and mitigate risks, which contribute to the success of a project.
4.2.4. Theme 4: Analysis of challenges and mitigation strategies of PM process
Project management involves various activities and vast operations, which often cause a lack of clear communication channels. It produces issues such as improper task distribution, unclear instructions, and undefined roles, which require establishing a platform that allows regular meetings and reviews. Establishing a clear communication channel allows coordinators to enhance communication among team members and reduce miscommunication (Shad et al. 2019). Utilising this approach not only helps to enhance communication channels but also allows the coordinator to manage a team effectively. Furthermore, coordinators can invest in communication tools, programs, and communication software. As project management involves various activities, this results in confusion due to a lack of clear project goals (Mishra, 2020). Addressing this issue required the involvement of smart criteria including relevant, measurable, achievable, specific and time-bound project goals. It helps coordinators to align the team with specific project objectives towards achieving success.
The introduction of KPI can help coordinators measure activities in PM, which can make sure that those actions are related to the project goals. The lack of accountability of action and activities in PM is another crucial challenge that hampers the efficiency of PM. Addressing this issue requires establishing a clear role and responsibility, which can bind the coordinator to work accordingly (Wu et al. 2019). Measuring the effectiveness of assigned roles and responsibilities requires reporting, which can ensure that individuals are fulfilling responsibilities properly. This is expected to help coordinators track the project’s progress and contribute to the success of the operations. The effectiveness of a team depends on the diverse skills and expertise, which ensure to fulfillment of all needs of a project (Mac Donald et al. 2020). A lack of team skills can severely affect the project and its success.
Mitigating this issue requires investment in training and exercise programs to develop team skills. Enhancing entire team skills also contributes to the coordinator’s efficiency, which eventually helps the project to achieve success. In addition, developing a culture of knowledge sharing can also increase team capabilities, which can help the coordinator achieve remarkable success in PM (Mishra, 2020). Another significant challenge that has the ability to negatively affect entire project efficiency is unrealistic deadlines. Addressing this issue requires providing realistic deadlines, which not only increases project efficiency but also reduces the pressure on coordinators and teams (Werner et al. 2021). The coordinator also needs to review the deadline carefully based on the achieved and pending work, which can help the coordination to divide work based on available time. It reduced work pressure and stress on the coordinator and contributed to increased efficiency of the project.
Exceeding project cost is another crucial challenge that a project faces due to various miscalculations and assumptions. Minimising this issue requires the coordinator a conduct a cost-benefit analysis, which can help to understand the project requirement and extension in the budget (Werner et al. 2021). It is expected to help the coordinator provide the exact project cost and complete the project within the allocated budget.
4.2.5. Theme 5: Application of advanced technology in reducing challenges of PM
Advanced technology has facilitated a significant change in the project management process, especially for project coordinators. One of the biggest challenges for the project coordinators is establishing a clear communication channel for all involved stakeholders in the project. Advanced technology has provided various tools and virtual platforms to collaborate with team members and clients. Maintaining ongoing communication with clients is easier with the use of virtual platforms as they allow people to keep in touch constantly. Virtual platforms and software also help project coordinators in keeping touch with team members, which facilitates collaboration and communication (Malav et al. 2020). The utilisation of advanced technology has made the communication process of PM easier for the project coordinator, which can help reduce the scope of misunderstanding and increase efficiency.
Additionally, various cloud software and cloud technologies help in acquiring real-time data about the project’s progress. The essential documents and project progress reports can be uploaded to cloud platforms to ensure easy access to the clients and team members. It helps in informing the real-time status of the project and helps in ensuring employees have the required information to perform adequately during the project (Vrontis et al. 2022). Project coordinators can easily track the challenges and the real reason behind them, which ensures fast resolutions. AI has revolutionised the business industry, creating a significant impact on the project process as well. AI is generally used in analysing the real-time data received from the PM process to ensure optimised use of resources (Pan and Zhang, 2021). Project coordinators can use AI to analyse the requirements of the project regarding workforce, skills, and budget.
Moreover, AI can automate administrative tasks, which reduces the pressure on project coordinators. It also allows the effective development of the project as it only requires data input into the system to ensure appropriate results. On the other hand, Machine Learning or ML effectively complete repetitive tasks, which reduces the pressure of tasks on the team member. Project coordinators can utilise ML to complete repetitive tasks, which can help save time and resources (Alaloul et al. 2020). It can assist project coordinators in utilising their workforce effectively for complicated tasks during various projects. Furthermore, the use of data analytics can help in making informed decisions during projects (Mansouri et al. 2020). Project coordinators are responsible for making decisions on required resources, budget allocation, and team management, which can be simplified by the application of data analytics for assessing available information.
4.3. Discussion
Project coordinators have a crucial role in the project management process as they are responsible for coordinating with clients, managing team members, and scheduling. The literature review has highlighted one of the main duties of project coordination, which is to maintain excellent communication with all project stakeholders (Fioravanti et al. 2020). The findings have highlighted building trusting relationships with clients and making sure their needs and expectations are met are the duties of project coordinators. It emphasises the value of using project management tools, holding daily meetings, doing reviews, and providing progress updates (Bahadorestani et al. 2020). These exercises demonstrate the critical role that effective communication plays in the project management process by empowering the project coordinator to oversee and meet client demands.
In the literature review, having experience in the PM process has been highlighted as an essential aspect as project coordinators can help their teams navigate the effective knowledge and expertise required for team management. Having knowledge and insight into the PM process from prior experience is beneficial for handling issues that arise during the management process (Ngo and Hwang, 2022). Findings have further delved into the essentiality of experience as it has informed the most important component of project coordinator can comprehend the criteria for adjustments, appropriate resource allocation, and needs by having relevant experience in a related field (Mikkelsen et al. 2020).
The literature review has asserted that project coordinators can face a number of difficulties due to poor communication, including uneven task distribution, ambiguous instructions, ill-defined responsibilities, and ambiguous objectives. Due to a lack of knowledge about the credibility of the team, ineffective communication results in incorrect task distribution (Den Hartog, 2019). The involvement of project management in several activities leads to a lack of clarity in project goals. Coordinators can ensure that PM activities are aligned with the project goals by measuring them with the aid of KPIs. It is supported by the findings of the research, which informs establishing a clear line of communication with all project stakeholders is one of the coordinators’ toughest problems (Rusakova et al. 2020). With the help of advanced technology, team members and clients can collaborate using a variety of tools and virtual platforms.
Virtual platforms facilitate regular connections, making it easier to maintain ongoing relationships with clients, which helps project coordinators maintain communication. Additionally, the findings have dealt with the literature gap by analysing the application of advanced technology in the PM process, Project managers can save time and costs by using machine learning (ML) to accomplish repetitive activities (Pan and Zhang, 2021). It can help project managers make efficient use of their labour force for challenging jobs across a range of projects. AI is typically utilised to analyse real-time data from the PM process in order to guarantee resource optimisation (Vrontis et al. 2022). AI can be used by project coordinators to assess the labour, skill, and financial requirements of the project. Utilising data analytics can also aid in making wise selections while working on a project.
4.4. Conclusion
The chapter has highlighted various themes based on the findings of the research based on challenges and mitigation strategies of project coordination. This chapter has informed the role of managing client involvement and expectation management in the PM process. It has highlighted that project coordinators can obtain positive project outcomes by managing the expectations and involvement of clients. Additionally, it has analysed various factors such as the ability to clear communication, organising skills, risk management, and monitoring along with the impact of experience and training in successful projects. The impact of advanced technologies such as data analytics, ML, and AI has been analysed in mitigating the common challenges of project coordination.
Chapter 5: Conclusion
5.1. Conclusion
The project coordinator plays a vital role in managing various project activities, planning, logistics and procurement. Communication and leadership are two of the most required skills in a project coordinator, which is essential for managing client relationship and leading employees. Additionally, skills such as organising, analysing risks, and utilising various project management tools can be essential for project coordinators. The project management process often suffers due to the lack of clear objectives, accountability, and quality management. It creates confusion among the employees, which affects productivity and efficiency during the project. Moreover, lack of communication between leaders and employees along with insufficient team skills are the primary reasons behind inadequate results in project management.
The application of various advanced technology can help in resolving these challenges. In recent years, AI has been widely used in the decision-making process by providing more profitable and agile strategies (Anastasiu et al. 2023). Various software, which are powered by AI have been able to analyse real-time data to enhance the process of resource deployment in a project management process. On the other hand, IoT things is another technology, which has revolutionised the process of project coordination. IoT things are various physical devices connected to a wireless network, which has been playing a vital role in the development of project management software (Azmat and Mubashir, 2023). It has assisted the firm in creating a user-friendly interface, which can be responsive to a variety of devices and create a centralised suite of tools and apps for projects facilitating collaboration within projects.
The findings of the research have highlighted the common skill requirement of the project management process and the application of advanced technology, which can assist in reducing the common challenges faced by the project coordinators. This research can be highly effective for business firms to analyse common challenges and required skills for their employees and project managers (Bernat et al. 2023). It has highlighted the application of AI and IoT tools along with other technologies to improve the overall efficiency of the project management process. As a result, business firms can evaluate the effectiveness of advanced technology in the project management process from this study.
5.2. Linking with Objectives
Linking with Objective 1
The first objective is a discussion of the role of project coordinators in the process of project management. The project coordinators play an essential role in building a strong connection with the clients by understanding their interests, expectations, and responsibilities. They also play an important role in establishing clear communication channels through reviews, status updates, and daily meetings (Vărzaru, 2022). The utilisation of project management tools enhances channel efficiency. Effective project coordination involves collaboration with various stakeholders to build strong relationships to achieve project success. The communication and relationship allow clients to identify the changes in demands and requirements. Equipped with experience coordinators are capable of making effective decisions and designing mitigation plans.
They also focus on providing training to increase the knowledge and expertise to perform tasks such as analysis, planning, and decision-making. The experience of coordinators allows them to provide good leadership, which allows them to align the team with project objectives and work towards success (Zhang et al. 2023). Project coordinators are also responsible for identifying challenges such as lack of accountability, unclear project goals, team skill gaps, and communication issues in project management. Incorporating advanced technology such as cloud technologies in project management also comes under the responsibility of coordinators.
Linking with Objective 2
The second objective focuses on the skills and expertise that a project coordinator needs to have in terms of effectively managing the tasks in the project management process. Communication skills are one of the effective skills that a project coordinator needs to have to deliver the project objectives, goals, and expectations. In terms of building an effective team, leadership skills play an essential role. Similarly, the coordinator also needs to have organisational skills such as knowledge about flowcharts and diagrams (Khan et al. 2023). Experience is also considered an essential skill, which aids in making decisions and identifying challenges. Coordinators also possess skills regarding the methodologies of project management and best practices.
The project involves various activities and tasks, which cause conflict and addressing the conflicts is one of the essential skills of a project coordinator. The coordinator is also responsible for identifying and addressing risks through assessment, planning, monitoring, and learning from risks (Muneer et al. 2022). An effective coordinator encourages team coordination and technological adaptation, which increases team effectiveness. The skills of data analysis also help coordinators to make informed decisions, which include resources, budget allocation, and team management.
Linking with Objective 3
The third objective analyses the obstacles that influence project management and elements in the process. The lack of communication channels in project management can cause various difficulties such as improper task distribution, unclear instructions, and undefined responsibilities. The absence of implementation of smart goals causes confusion about project goals, which leads to the waste of resources and time (Anastasiu et al. 2023). An unclear responsibility causes a lack of accountability in project management, which decreases the effectiveness of project outcomes. The lack of diversity in team skills and expertise can severely affect the success of the project and lead to failure. Deadline is one of the primary elements that can influence the entire project management process.
An unrealistic deadline can severely affect the project’s effectiveness and success. An unorganised project plan can lead to an increase in the project cost, which can affect the client’s satisfaction and reflect a failed project (Azmat and Mubashir, 2023). A team with a lack of skills can barely able to conduct a cost-benefit analysis and lead to a position where the coordinator has limited knowledge regarding the project cost. Ineffective use of technologies and resistance to change are also considered project obstacles.
Linking with Objective 4
The fourth objective discusses the mitigation plans to address challenges that occur during project implementation stages. Addressing communication challenges requires establishing and maintaining communication channels, conducting regular interviews, and investing in communication tools, programs, and software. The project coordinator needs to introduce relevant, measurable, achievable, specific, and time-bound project goals for better goal understanding (Ichsan et al. 2023). The project manager needs to establish clear goals and responsibilities to aware the teams regarding their task, which can help to address the issue related to accountibility. Addressing the lack of skills and expertise in various grounds of project management requires providing training and personal development programs (Azmat and Mubashir, 2023). It not only helps coordinators to enhance the team’s effectiveness but also increases the success of the project.
The project requires a realistic deadline, which can be done by carefully reviewing project dimensions and pending work. The project management tools can address the issue of increasing project costs by tracking project expenses. Implementation of training programs for advanced technology such as virtual platforms, cloud technology, AI, and ML increases the chances of cooperating with change management strategies (Taboada et al. 2023). Furthermore, the adaptability of continuous learning can enhance the utilisation of advanced technologies.
5.3. Recommendations
The project coordinators need to have adequate knowledge and experience regarding using advanced technology such as AI, ML, and IoT things in the project management process. In recent years, the implementation of advanced technology in project coordination has become common among business organisations (Bugarčić and Slavković, 2023). The integration of AI and ML has assisted in making informed decisions and analysing a large amount of data in less time. It has also assisted in automating various repetitive tasks, which has reduced pressure on the workforce. Additionally, IoT devices have provided an overview of real-time data regarding the project tasks (Hamsal et al. 2022). Hence, project coordinators need to obtain practical experience and substantial knowledge regarding the implementation of advanced technology in the project process.
Additionally, these tools can also be used in assessing risks, which are associated with the project, which can assist in resource allocation to overcome emerging obstacles. Risk assessment is an essential part of project management as it helps the project coordinator evaluate the scope of challenges and their severity (Ichsan et al. 2023). It helps in managing schedules and resources to maintain adequate client satisfaction. On the other hand, the application of IoT devices helps in providing clients with faster updates regarding the project’s progress. As a result, it ensures effective and efficient communication leading to higher satisfaction among clients (Bernat et al. 2023). In this way, project coordinators are able to manage the expectations of the clients in an adequate manner. Furthermore, the application of cloud technology can help the project coordinator in establishing a collaborative platform with the involved staff members, which can increase efficiency and overall performance.
5.4. Limitations
This research has integrated a secondary research approach, which has enabled data collection from secondary sources. It has helped in reducing the time for data collection and provided a strong foundation for research. However, it has restricted the collection of data directly from the participants regarding the challenges of project management. It can be considered as a limitation of the study as it could have provided a diverse perspective on the challenges and ways to mitigate the problems in the project management process. The application of primary data collection through an interview process could have provided an in-depth understanding of the challenges of project coordination.
5.5. Future research questions
The future research questions highlight the scope for further research on this topic.
- What role does emerging technology play in overcoming project coordination and project implementation?
- How do the external factors affect the process of project management?
- What project management methodologies can be implemented to mitigate the problems of project coordination?
- How effective is the risk assessment in mitigating uncertain events during the project implementation process?
6. Reflection
During the internship at AHNAIZN Business Group and this project, I have gained an extended knowledge about project coordinator and their responsibilities. I have joined the organisation as an intern in a project coordinator position, which has allowed me to learn about a wide range of responsibilities and activities, a project coordinator has within an organisation. Moreover, during the research on identifying the challenges of project coordination and their resolution, I have gained in-depth knowledge about the project coordination process. Through the application of Gibbs’ reflective model, I have analysed my personal experience starting from the internship to the completion of this project.
The Gibbs’ reflective cycle facilitates experience-based learning due to its cyclic nature. It helps individuals gain insight into an event by analysing the activities and responses of people involved in the event (Adeani et al. 2020). Hence, the application of Gibbs’ model can help me in systematically analysing my learning and drawbacks to determine a suitable action plan for similar future events. The Gibbs’ model consists of six distinct stages: description, feeling, evaluation, analysis, conclusion, and action plan.
Figure 6.1: Gibbs’ Reflective Cycle
(Source: Adeani et al. 2020)
Description
During my internship as a project coordinator, I have been responsible for maintaining deadlines for various projects. I have scheduled entire projects segmenting them into smaller tasks to complete the entire project before the deadline. I also managed finances for the projects and interacted with the clients to ensure positive satisfaction. The role of the project coordinator also includes adequate coordination of teams and maintaining confidential documents, communication with the stakeholders, and handling clients’ information (Karlsen et al. 2020). Managing various tasks related to project management has helped me learn about the varied responsibilities and activities of a project coordinator. On the other hand, during the research on the challenges of project coordination, I have done an in-depth analysis of the role of project coordinator and the required skills for this position.
The project coordinator is a vital aspect of the project management process as the project coordinator ensures adequate progress of the projects by overseeing various activities, allocating resources, and comprehending the requirements of the projects (Henkel et al. 2019). The learning during my research has aligned with my first-hand experience of acting as an intern project coordinator. In my opinion, a project coordinator helps in simplifying complex projects by understanding the requirements and segmenting them into smaller tasks along with allocating suitable resources to the successful completion of the entire project. Additionally, effective knowledge and experience have emerged as the most required skills in project coordinators (Lehtinen and Aaltonen, 2020). It highlights the essentiality of adequate experience in handling various projects and obtaining in-depth knowledge.
I think the internship at the AHNAIZN Business Group has provided me with significant experience as a project coordinator. It has helped me gain adequate experience in handling various projects and collaborating with team members. One of the primary skills, which is required in a project coordinator is communication. A project coordinator needs to have effective communication skills to maintain a positive relationship with the clients and collaborate with the team members (Alvarenga et al. 2019). The internship has helped me improve my communication skills substantially as I was responsible for interacting with the client and team members daily. Moreover, I have gained significant knowledge about the common challenges of project coordination and suitable mitigation strategies. Lack of communication, accountability, and inability to set clear objectives are often primary reasons behind project management failure.
The research has provided insight into various mitigation strategies such as utilising KPIs and SMART criteria for analysing the performance of the team members to facilitate continuous monitoring and improvement. Along with that, the establishment of communication tools can help reduce communication problems between the project coordinator and involved team members in a project (Silvius and de Graaf, 2019). I have also analysed the importance of experience management and client involvement, in which the project coordinator plays a significant role in regularly interacting with the clients. In my opinion, the application of various advanced technologies such as cloud technology and AI can help in mitigating the common challenges of project coordination.
Feeling
I feel satisfied regarding my experience at AHNAIZN Business Group as it has provided me with the necessary experience and skills to become a successful project coordinator. I feel that my experience as an intern has helped me in researching challenges of mitigation strategies of project coordination. I have analysed the impact of training and experience in successful project completion. Experience project coordinator can easily analyse risks associated with the project and create effective strategies to reduce their impact on the project (Malucelli et al. 2021). As per my understanding, training, and experience play a crucial role in project success.
Evaluation
Overall, I had a good experience during my internship and my research. I have acquired help from the senior staff during the internship at AHNAIZN, which has provided me with practical knowledge. During my research, I have been able to use my learning from the internship. However, I have often stressed during the research due to time constraints. I have often worried about the completion of the research project on time.
Analysis
I think I need to improve my time management skills to improve my capabilities while multitasking. I was stressed during the research as I had to manage classes, various activities, and personal obligations. Time management can help me in creating an effective schedule for various tasks.
Conclusion
In my opinion, making a schedule could have helped me in managing my activities efficiently. It could have provided me with an understanding of the smaller activities required for this research and the required time for each activity.
Action plan
I have decided to improve my time management skills by learning various factors of time management from books and the Internet. Prioritisation can be one of the most effective techniques, which allows people to determine the sequence of activities based on their importance (Bajec, 2019). It can help me in completing essential tasks first giving me time for taking smaller breaks within activities. I think it can increase my efficiency and development.
References
Abou-Shouk, M. and Soliman, M., 2021. The impact of gamification adoption intention on brand awareness and loyalty in tourism: The mediating effect of customer engagement. Journal of Destination Marketing & Management, 20, p.100559.
Adeani, I.S., Febriani, R.B. and Syafryadin, S., 2020. Using GIBBS’reflective cycle in making reflections of literary analysis. Indonesian EFL Journal, 6(2), pp.139-148.
AHNAIZN, 2023. AHNAIZN – Business Group. [Online]. Available at: https://ahnaizn.com/ [Accessed on 26-10-2023]
Akbar, M.A., Sang, J., Khan, A.A. and Hussain, S., 2019. Investigation of the requirements change management challenges in the domain of global software development. Journal of Software: Evolution and Process, 31(10), p.e2207.
Al-Ababneh, M.M., 2020. Linking ontology, epistemology and research methodology. Science & Philosophy, 8(1), pp.75-91.
Alaloul, W.S., Liew, M.S., Zawawi, N.A.W.A. and Kennedy, I.B., 2020. Industrial Revolution 4.0 in the construction industry: Challenges and opportunities for stakeholders. Ain shams engineering journal, 11(1), pp.225-230.
Alvarenga, J.C., Branco, R.R., do Valle, A.B., Soares, C.A.P. and da Silveira, W., 2019. The self-perception of project managers compared to other project actors. Interciencia, 44(8), pp.444-453.
Alvarenga, J.C., Branco, R.R., Guedes, A.L.A., Soares, C.A.P. and da Silveira, W., 2019. The project manager core competencies to project success. International journal of managing projects in Business, 13(2), pp.277-292.
Anastasiu, L., Câmpian, C. and Roman, N. 2023, “Boosting Construction Project Timeline: The Case of Critical Chain Project Management (CCPM)”, Buildings, vol. 13, no. 5, pp. 1249.
Armenia, S., Dangelico, R.M., Nonino, F. and Pompei, A., 2019. Sustainable project management: A conceptualization-oriented review and a framework proposal for future studies. Sustainability, 11(9), p.2664.
Azmat, Z. and Mubashir, A.S. 2023, “Analyzing Project Complexity, Its Dimensions and Their Impact on Project Success”, Systems, vol. 11, no. 8, pp. 417.
Babii, A., 2020. Important aspects of the experimental research methodology. Вісник Тернопільського національного технічного університету, 97(1), pp.77-87.
Bahadorestani, A., Naderpajouh, N. and Sadiq, R., 2020. Planning for sustainable stakeholder engagement based on the assessment of conflicting interests in projects. Journal of Cleaner Production, 242, p.118402.
Bajec, B., 2019. Relationship between time perspective and time management behaviours. psihologija, 52(2), pp.197-215.
Bernat, G.B., Eduardo, L.Q. and Marcela, S.C. 2023, “Enhancing Sustainability in Project Management: The Role of Stakeholder Engagement and Knowledge Management in Virtual Team Environments”, Sustainability, vol. 15, no. 6, pp. 4896.
Bernat, G.B., Eduardo, L.Q., Marcela, S.C., André, B.B. and Raquel, R.S. 2023, “Sustainability in Project Management and Project Success with Virtual Teams: A Quantitative Analysis Considering Stakeholder Engagement and Knowledge Management”, Sustainability, vol. 15, no. 12, pp. 9834.
Budianto, A., 2020. Legal research methodology reposition in research on social science. International Journal of Criminology and Sociology, 9(1), pp.1339-1346.
Bugarčić, M. and Slavković, M. 2023, “Does Digitalization Supports Project Management Effectiveness? New Insight on the Role of Intellectual Capital”, Buildings, vol. 13, no. 8, pp. 1898.
Chernogorova, Y., Bliznakov, Z. and Bliznakova, K., 2021. Management challenges in implementing scientific projects during COVID-19 pandemic. Polish Journal of Management Studies, 23(1), pp.136-150.
Chivanga, S.Y. and Monyai, P.B., 2021. Back to basics: Qualitative research methodology for beginners. Journal of Critical Reviews, 8(2), pp.11-17.
Cunningham, J.A. and O’Reilly, P., 2019. Roles and responsibilities of project coordinators: a contingency model for project coordinator effectiveness (No. JRC117576). Joint Research Centre (Seville site).
de Almeida Parizotto, L., Tonso, A. and de Carvalho, M.M., 2020. The challenges of project management in small and medium-sized enterprises: a literature review based on bibliometric software and content analysis. Gestão & Produção, 27, p.e3768.
Delios, A., Welch, C., Nielsen, B., Aguinis, H. and Brewster, C., 2023. Reconsidering, refashioning, and reconceptualizing research methodology in international business. Journal of World Business, 58(6), p.101488.
Derakhshan, R., Turner, R. and Mancini, M., 2019. Project governance and stakeholders: a literature review. International Journal of Project Management, 37(1), pp.98-116.
Djafar, H., Yunus, R., Pomalato, S.W.D. and Rasid, R., 2021. Qualitative and Quantitative Paradigm Constellation In Educational Research Methodology. International Journal of Educational Research and Social Sciences (IJERSC), 2(2), pp.339-345.
Dodds, S. and Hess, A.C., 2020. Adapting research methodology during COVID-19: lessons for transformative service research. Journal of Service Management, 32(2), pp.203-217.
Dzwigol, H., 2022. Research methodology in management science: Triangulation. Virtual Economics, 5(1), pp.78-93.
Farashah, A.D., Thomas, J. and Blomquist, T., 2019. Exploring the value of project management certification in selection and recruiting. International Journal of Project Management, 37(1), pp.14-26.
Fioravanti, M.L., Sena, B. and Barbosa, E.F., 2020, October. Assessing the development of soft skills for project management using PBL: a case study. In 2020 IEEE Frontiers in Education Conference (FIE) (pp. 1-8). IEEE.
Friedrich, K., 2023. A systematic literature review concerning the different interpretations of the role of sustainability in project management. Management Review Quarterly, 73(1), pp.31-60.
Giglioni, G.B. and Bedeian, A.G., 2019. A conspectus of management control theory: 1900-1972. In Management Control Theory (pp. 3-16). Routledge.
Greening, N., 2019. Phenomenological research methodology. Scientific Research Journal, 7(5), pp.88-92.
Haass, O. and Azizi, N., 2020. Challenges and solutions across project life cycle: A knowledge sharing perspective. International Journal of Project Organisation and Management, 12(4), pp.346-379.
Hamsal, M., Dwidienawati, D., Ichsan, M., Syamil, A. and Trigunarsyah, B. 2022, “Multi-Perspective Approach to Building Team Resilience in Project Management—A Case Study in Indonesia”, Sustainability, vol. 14, no. 20, pp. 13137.
Henkel, T.G., Marion Jr, J.W. and Bourdeau, D.T., 2019. Project manager leadership behavior: Task-oriented versus relationship-oriented. Journal of Leadership Education, 18(2), p.1.
Henkel, T.G., Marion Jr, J.W. and Bourdeau, D.T., 2019. Project manager leadership behavior: Task-oriented versus relationship-oriented. Journal of Leadership Education, 18(2), p.1.
Hussain, N., HAQUE, A.U. and Baloch, A., 2019. Management theories: The contribution of contemporary management theorists in tackling contemporary management challenges. Yaşar Üniversitesi E-Dergisi, 14, pp.156-169.
Ichsan, M., Hamsal, M. and Abdinagoro, S.B. 2023, “The Role of Project Management Office in Managing Project Portfolio Management: A Descriptive Study in Indonesian Banks”, Global Business & Finance Review, vol. 28, no. 2, pp. 45-52.
Iovino, F. and Tsitsianis, N., 2020. The methodology of the research. In Changes in European energy markets (pp. 79-95). Emerald Publishing Limited.
Kabeyi, M.J.B., 2020. Project and program evaluation consultancy with terms of reference, challenges, opportunities, and recommendations. International Journal of Project Management and Productivity Assessment (IJPMPA), 8(2), pp.47-68.
Kamal, S., 2020. Importance of Scientific Management in the Modern Management. Black Sea Journal of Management and Marketing, 1(2), pp.45-53.
KANG, E. and Hwang, H.J., 2021. Ethical conducts in qualitative research methodology: Participant observation and interview process. Journal of Research and Publication Ethics, 2(2), pp.5-10.
Karlsen, J.T., Farid, P. and Torvatn, T., 2020. Project manager roles in a public change project: the case of a municipal merger. International Journal of Organization Theory & Behavior, 23(2), pp.155-171.
Keegan, A. and Den Hartog, D., 2019. Doing it for themselves? P erformance appraisal in project‐based organisations, the role of employees, and challenges to theory. Human Resource Management Journal, 29(2), pp.217-237.
Khan, G.M., Khan, S.U., Khan, H.U. and Ilyas, M., 2022. Challenges and practices identification in complex outsourcing relationships: A systematic literature review. PloS one, 17(1), p.e0262710.
Khan, U.U., Yousaf, A., Garai-Fodor, M. and Csiszárik-Kocsir, Á. 2023, “Application of Project Management Techniques for Timeline and Budgeting Estimates of Startups”, Sustainability, vol. 15, no. 21, pp. 15526.
Khosravi, P., Rezvani, A. and Ashkanasy, N.M., 2020. Emotional intelligence: A preventive strategy to manage destructive influence of conflict in large scale projects. International Journal of Project Management, 38(1), pp.36-46.
Larsson, J. and Larsson, L., 2020. Integration, application and importance of collaboration in sustainable project management. Sustainability, 12(2), p.585.
Lee, K.T., Ahn, H. and Kim, J.H., 2023. Project Coordinators’ Perceptions according to the Organization Structure to Reduce Communication Risks in Multinational Project. KSCE Journal of Civil Engineering, 27(3), pp.915-929.
Lehtinen, J. and Aaltonen, K., 2020. Organizing external stakeholder engagement in inter-organizational projects: Opening the black box. International Journal of Project Management, 38(2), pp.85-98.
Lehtinen, J. and Aaltonen, K., 2020. Organizing external stakeholder engagement in inter-organizational projects: Opening the black box. International Journal of Project Management, 38(2), pp.85-98.
Mac Donald, K., Rezania, D. and Baker, R., 2020. A grounded theory examination of project managers’ accountability. International Journal of Project Management, 38(1), pp.27-35.
Malav, L.C., Yadav, K.K., Gupta, N., Kumar, S., Sharma, G.K., Krishnan, S., Rezania, S., Kamyab, H., Pham, Q.B., Yadav, S. and Bhattacharyya, S., 2020. A review on municipal solid waste as a renewable source for waste-to-energy project in India: Current practices, challenges, and future opportunities. Journal of Cleaner Production, 277, p.123227.
Malucelli, G., Barbosa, M.T. and Carvalho, M.M.D., 2021. Facing the challenge of improvisation in project management: A critical review. International Journal of Managing Projects in Business, 14(2), pp.369-389.
Mansouri, S., Castronovo, F. and Akhavian, R., 2020. Analysis of the synergistic effect of data analytics and technology trends in the AEC/FM industry. Journal of Construction Engineering and Management, 146(3), p.04019113.
Martinsuo, M. and Geraldi, J., 2020. Management of project portfolios: Relationships of project portfolios with their contexts. International Journal of Project Management, 38(7), pp.441-453.
Marx, S., 2023. Mapping as critical qualitative research methodology. International Journal of Research & Method in Education, 46(3), pp.285-299.
Mikkelsen, M.F., Marnewick, C. and Klein, L., 2020. On Stupidity in Project Management-A critical reflection of PM in a VUCA world. The Journal of Modern Project Management, 8(2).
Mishra, A.K., 2020. Implication of theory of constraints in project management. International Journal of Advanced Trends in Engineering and Technology, 5(1), pp.1-13.
Moradi, H. and Shadrokh, S., 2019. A robust scheduling for the multi-mode project scheduling problem with a given deadline under uncertainty of activity duration. International Journal of Production Research, 57(10), pp.3138-3167.
Muneer, M., Khan, N., Muhammad, A.H., Zhang, S., Adnan, A.K., Farooq, R., Moawwez, M.A. and Muhammad Atiq Ur, R.T. 2022, “A Quantitative Study of the Impact of Organizational Culture, Communication Management, and Clarity in Project Scope on Constructions’ Project Success with Moderating Role of Project Manager’s Competencies to Enhance Constructions Management Practices”, Buildings, vol. 12, no. 11, pp. 1856.
Newman, M. and Gough, D., 2020. Systematic reviews in educational research: Methodology, perspectives and application. Systematic reviews in educational research: Methodology, perspectives and application, pp.3-22.
Ngo, J. and Hwang, B.G., 2022. Critical Project Management knowledge and skills for managing projects with smart technologies. Journal of Management in Engineering, 38(6), p.05022013.
Ocaña-Fernández, Y. and Fuster-Guillén, D., 2021. The bibliographical review as a research methodology. Revista Tempos E Espaços Em Educação, 14(33), pp.e15614-e15614.
Pan, Y. and Zhang, L., 2021. Roles of artificial intelligence in construction engineering and management: A critical review and future trends. Automation in Construction, 122, p.103517.
Patel, M. and Patel, N., 2019. Exploring research methodology. International Journal of Research and Review, 6(3), pp.48-55.
Peña, A.R. and Muñoz, F.A., 2020. Soft skills as a critical success factor in project management. In Handbook of Research on Project Management Strategies and Tools for Organizational Success (pp. 376-392). IGI Global.
Perez-Encinas, A., de Pablo, I., Bueno, Y. and Santos, B., 2021. Intergenerational entrepreneurship to Foster sustainable development: A methodological training proposal. Sustainability, 13(17), p.9654.
Puška, A., Stojanović, I., Maksimović, A. and Osmanović, N., 2020. Evaluation software of project management by using measurement of alternatives and ranking according to compromise solution (MARCOS) method. Operational Research in Engineering Sciences: Theory and Applications, 3(1), pp.89-102.
References
Rusakova, T., Muss, G., Miroshnikova, D. and Kucheruk, D., 2020. In-company training in lifelong learning. In ICERI2020 Proceedings (pp. 3730-3739). IATED.
Ryder, C., Mackean, T., Coombs, J., Williams, H., Hunter, K., Holland, A.J. and Ivers, R.Q., 2020. Indigenous research methodology–weaving a research interface. International Journal of Social Research Methodology, 23(3), pp.255-267.
Saesen, R., Machado, M., Crifo, B., Liu, L., de Vries, C., Herold, R., Llinares Garcia, J. and Huys, I., 2023. Involvement of the European Medicines Agency in multi-stakeholder regulatory science research projects: experiences of staff members and project coordinators. Frontiers in Medicine, 10, p.1181702.
Safapour, E., Kermanshachi, S., Taneja, P. and Pamidimukkala, A., 2022. Exploratory analysis of human-, organizational-, and project-based reworks: Challenges and strategies. Journal of Legal Affairs and Dispute Resolution in Engineering and Construction, 14(1), p.04521045.
Salvador, F., Alba, C., Madiedo, J.P., Tenhiälä, A. and Bendoly, E., 2021. Project managers’ breadth of experience, project complexity, and project performance. Journal of Operations Management, 67(6), pp.729-754.
Secundo, G., Elia, G., Margherita, A. and Leitner, K.H., 2022. Strategic decision making in project management: a knowledge visualization framework. Management Decision, 60(4), pp.1159-1181.
Senabre Hidalgo, E. and Fuster Morell, M., 2019. Co-designed strategic planning and agile project management in academia: Case study of an action research group. Palgrave Communications, 5(1), pp.1-13.
Shad, F., Shah, F.A., Jan, S. and Ahmad, S., 2019. Importance of communication in project management: A case study of communication & works department Peshawar. Sarhad Journal of Management Sciences, 5(2), pp.267-280.
Shpeizer, R., 2019. Towards a successful integration of project-based learning in higher education: Challenges, technologies and methods of implementation. Universal Journal of Educational Research, 7(8), pp.1765-1771.
Sileyew, K.J., 2019. Research design and methodology. Cyberspace, pp.1-12.
Silvius, A.G. and de Graaf, M., 2019. Exploring the project manager’s intention to address sustainability in the project board. Journal of cleaner production, 208, pp.1226-1240.
Snyder, H., 2019. Literature review as a research methodology: An overview and guidelines. Journal of business research, 104, pp.333-339.
Stanitsas, M., Kirytopoulos, K. and Leopoulos, V., 2021. Integrating sustainability indicators into project management: The case of construction industry. Journal of Cleaner Production, 279, p.123774.
Stonehouse, G.H. and Konina, N.Y., 2020, February. Management challenges in the age of digital disruption. In 1st International Conference on Emerging Trends and Challenges in the Management Theory and Practice (ETCMTP 2019) (pp. 1-6). Atlantis Press.
Taboada, I., Daneshpajouh, A., Toledo, N. and de Vass, T. 2023, “Artificial Intelligence Enabled Project Management: A Systematic Literature Review”, Applied Sciences, vol. 13, no. 8, pp. 5014.
Taneja, K., 2022. Employing project-based learning to foster essential professional skills in students of graphic design. IDA: International Design and Art Journal, 4(2), pp.173-184.
Tayebi Abolhasani, A., 2019. Introduction to research methodology: Standard procedures for qualitative data analysis. Science and Technology Policy Letters, 9(2), pp.67-96.
Taylor, F.W., 2023. the Rise of Scientific Management. The Quantified Worker: Law and Technology in the Modern Workplace, p.9.
Tee, R., Davies, A. and Whyte, J., 2019. Modular designs and integrating practices: Managing collaboration through coordination and cooperation. Research policy, 48(1), pp.51-61.
Tereso, A., Ribeiro, P., Fernandes, G., Loureiro, I. and Ferreira, M., 2019. Project management practices in private organizations. Project Management Journal, 50(1), pp.6-22.
Tominc, P., Oreški, D. and Rožman, M. 2023, “Artificial Intelligence and Agility-Based Model for Successful Project Implementation and Company Competitiveness”, Information, vol. 14, no. 6, pp. 337.
Tran, N.Q., Carden, L.L. and Zhang, J.Z., 2022. Work from anywhere: remote stakeholder management and engagement. Personnel Review, 51(8), pp.2021-2038.
Urcia, I.A., 2021. Comparisons of adaptations in grounded theory and phenomenology: Selecting the specific qualitative research methodology. International journal of qualitative methods, 20, p.16094069211045474.
Vaagaasar, A.L., Hernes, T. and Dille, T., 2020. The challenges of implementing temporal shifts in temporary organizations: Implications of a situated temporal view. Project Management Journal, 51(4), pp.420-428.
Vărzaru, A.A. 2022, “An Empirical Framework for Assessing the Digital Technologies Users’ Acceptance in Project Management”, Electronics, vol. 11, no. 23, pp. 3872.
Vrontis, D., Christofi, M., Pereira, V., Tarba, S., Makrides, A. and Trichina, E., 2022. Artificial intelligence, robotics, advanced technologies and human resource management: a systematic review. The International Journal of Human Resource Management, 33(6), pp.1237-1266.
Werner, C., Li, Z.S., Lowlind, D., Elazhary, O., Ernst, N. and Damian, D., 2021. Continuously managing nfrs: Opportunities and challenges in practice. IEEE Transactions on Software Engineering, 48(7), pp.2629-2642.
Willmott, H., 2020. On research methodology. The Journal of Organization and Discourse, 1(1), pp.1-4.
Workineh, N.A., 2022. Investigating the most essential skills of planners in Ethiopia’s Amhara National Regional State’s Regiopolitan cities. Journal of Innovation and Entrepreneurship, 11(1), pp.1-15.
Wu, G., Hu, Z. and Zheng, J., 2019. Role stress, job burnout, and job performance in construction project managers: the moderating role of career calling. International journal of environmental research and public health, 16(13), p.2394.
Zawacki-Richter, O., Kerres, M., Bedenlier, S., Bond, M. and Buntins, K., 2020. Systematic reviews in educational research: Methodology, perspectives and application (p. 161). Springer Nature.
Zhang, L., Mohandes, S.R., Tong, J., Abadi, M., Banihashemi, S. and Deng, B. 2023, “Sustainable Project Governance: Scientometric Analysis and Emerging Trends”, Sustainability, vol. 15, no. 3, pp. 2441.
