Employee Retention Strategy of HRM in Ahnaizn Business Group
Abstract
The aim of this research is to analyse and assess the staff retention plan implemented by AHNAIZN Business Group. The research background and rationale are highlighted in the chapter 1 along with the problem description, significance, and research questions. The objectives and research questions have identified the study areas. Along with a graphic illustration of the dissertation format, the chapter also includes a problem statement, justification, and the importance of the research.
The chapter 2 analyses the staff retention strategy adopted by the HRM department of AHNAIZN Group by drawing on a variety of previous research articles and periodicals. It draws attention to a number of HRM and employee retention strategy principles, as well as the conceptual framework, theoretical application, and gap in the literature.
The chapter 3 explains and justifies the research strategies utilised to acquire information on the employee retention techniques of HRM in AHNAIZN Business Group. In this study, a mixed approach has been employed to combine both qualitative and quantitative data. A survey has been used to acquire primary quantitative data from 30 employees of the company.
The chapter 4 offers a comprehensive examination of the survey outcomes and a thematic examination of the secondary data, so enabling a discourse on the efficaciousness of human resource management in the context of employee retention. The results of the thematic analysis of secondary data were connected to the survey results through discussion.
Chapter 5 highlights an overall summary of the research regarding the employee retention strategy of the HRM department of AHNAIZN Business Group. This chapter includes links with objectives, recommendations, limitations, and future research scope. This research can be significant to small and medium-sized businesses in improving their employee retention strategies.
Chapter 1: Introduction
1.1. Introduction
Employee retention strategy is the planned approach of an organisation to prevent attrition, reduce employee turnover, and facilitate employee engagement. Employee retention is an essential part of HRM, which helps business firms effectively manage their workforce and enhance employee engagement. AHNAIZN Business Group is a popular branding and marketing research firm, which provides business solutions to SMEs in the UK. The firm provides unique ideas for digital businesses and invests in “wholesale fashion”, “online fashion”, and various consultation projects. The research analyses AHNAIZN’s employee retention strategy. This chapter highlights research questions, objectives, significance, and problem statement along with research background and rationale.
1.2. Research background
HRM is a crucial part of an organisation in terms of maintaining its workforce and productivity. In addition, employee retention is one of the elements of HRM, which ensures that the business can reduce its turnover rate. Employee satisfaction plays a crucial role in increasing retention rate by enhancing employees’ happiness including employee safety and security and incentives on performance (Ramapriya and Sudhamathi, 2020). Companies such as AHNAIZN have also focused on providing holidays and leaves to maintain a sustainable work environment, which not only helps the firm to increase retention rate but also fulfils CSR. The high rate of retention shows various positive aspects of an organisation inducing employee satisfaction, providing solutions for the workforce, and solving the organisation’s cultural issues (Papa et al. 2020).
Noticing a high turnover rate indicates the incredibility of the HRM process of an organisation, which can be caused by various negative factors. One of the primary responsibilities of HRM is to provide an effective and skilled workforce to the organisation, which can assist the firm in gaining progress (Sepahvand and Bagherzadeh Khodashahri, 2021). HRM also plays a significant role in providing or arranging training programs, which can enhance employee skills and increase knowledge regarding technologies. These training programs also help to increase employee reliability and effectiveness, which allows an organisation to have an effective workforce to achieve success. Employee retention rate also influences the company image, which can encourage or discourage the new entrance (Okbagaber, 2019). Therefore, HRM focuses on employee retention due to the impact of the mouth of word by employees on the organisation.

Figure 1.1: Factors of employee motivation in retention strategy
(Source: Okbagaber, 2019)
Recruiting new employees consume more time and resources to learn about the company’s goal, vision, and objectives, while experienced employees can perform their job based on the specific organisational knowledge they already have. The significance of the workers’ experience and knowledge that old employees already have make them valuable to the company, which shows the importance of a high retention rate (Jam and Jamal, 2020). The company AHNAIZN has focused on various employees’ motivational factors such as “achievement”, “recognition”, “job satisfaction”, “responsibility”, “advancement”, and “growth” (Okbagaber, 2019). Completing organisational tasks and achieving goals encourage employees to keep engaged with the firm. Recognising employees for their efforts also motivates employees. Job satisfaction and divided responsibility are also considered motivational factors for high retention rates (Jacob, 2021). Providing opportunities for career improvement allows employees to be confident and increase their motivation. Skill development and training programs help in personal development, which motivate employees and increase retention rate.
1.3. Research aim and objectives
Aim
The aim of the research is to discuss and evaluate the employee retention strategy adopted by AHNAIZN Business Group.
Objectives
● To examine the role of a HR intern in fostering the people function in the firm
● To evaluate the CSR activities and organisational performances of the firm to facilitate employee satisfaction
● To analyse the recruitment process for interns facilitated by the HRM team of AHNAIZN Business Group
● To determine the role of organisational culture regarding the inclusion of new employees in the organisation
1.4. Research questions
● What role does an HR intern play in developing the people function in AHNAIZN Business Group?
● How does AHNAIZN Business Group develop their CSR activities and organisation performance to increase employee satisfaction?
● What is the recruitment procedure employed by the HRM department of the company?
● How does organisational culture help in including new employees in the business firm?
1.5. Problem statement
Maintaining a positive retention rate has various challenges, which increase the overall turnover rate in organisations. One of the significant challenges that employees face is the lack of “opportunities for career development”, which caused approximately 41% of resignations (Statista, 2023). In addition, 65% of employees who have already served a specific industry and left their jobs due to a lack of “career development facilities” have never re-joined a similar sector. Additionally, the issue of “inadequate compensation” has also become the reason for leaving jobs for approximately 36% of cases. It shows that organisations are mainly focused on profitability rather than employee satisfaction, which can considered as a failed HRM (Jacob, 2021). The lack of development opportunities and insufficient compensation are affecting the employee’s motivational factors, which not only increases the turnover rate but also decreases the organisational growth.
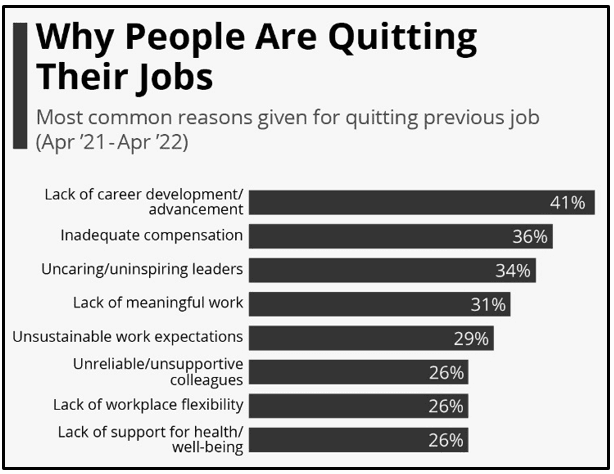
Figure 1.2: Challenges of employee retention
(Source: Statista, 2023)
Furthermore, an “uninspiring leader” also influences employee retention rate by affecting employee recognition. Approximately, 34% of employee resignations are caused by defaulter leaders, which shows that the HRM process has failed in maintaining a positive employee motivational culture within the company (Statista, 2023). Overall, motivational factors such as “recognition”, “advancement”, and “growth” play a significant role in the industries for increasing turnover rate.
1.6. Rationale
Employee retention strategies generally help provide employees with higher job satisfaction to reduce employee turnover, which helps the firms optimise the cost of hiring and training (Hassan et al. 2019). HRM departments of the firms play a crucial role in employee retention, as they are responsible for integrating regulations and strategies to offer career opportunities and scope of learning to facilitate employee satisfaction (Sawaneh and Kamara, 2019). As a result, employee retention strategies assist in enhancing employee productivity and establishing adequate work relationships, which in turn reduces stress and the probability of burnout (Hassan, 2022). There are several literary works available, which examine the employee retention strategies of HRM. However, the employee retention strategies employed by the HRM of AHNAIZN Business Group have not been examined in a comprehensive manner.
AHNAIZN is a popular UK firm, which provides consultation services for other businesses and clients (AHNAIZN, 2023). It employs 11-50 employees and has recently expanded its business in retail and fashion. The analysis of the employee retention strategy of the firm can help in understanding the effective strategies for maintaining employee satisfaction in small firms (Okbagaber, 2019). It can help other UK firms obtain knowledge from AHNAIZN and their HRM group to maintain lower stress levels and avoid employee burnout in their workplaces. As a result, conducting research on the employee retention strategies of AHNAIZN is highly relevant to analysing the strategies of SMEs in the UK.
1.7. Significance of research
The significance of this research lies in the importance of HRM and its policies to maintain positive employee retention rates. The study has highlighted various factors that influence the retention rate both positively and negatively. In addition, the understanding of the importance of HRM and the retention rate has provided valuable insights regarding workforce management (Sawaneh and Kamara, 2019). The implementation of practices that increase employee motivation has also shown various positive sites, which can help industries to increase their retention rate. The outcomes of this research on AHNAIZN’s HRM can help UK-based companies learn the importance of HRM. Utilising the outcome and information of this research can help other companies reduce work pressure and enhance employees’ motivation. Therefore, this research is expected to play a crucial role in UK-based SME companies’ ability to develop effective employee management strategies.
1.8. Structure of dissertation
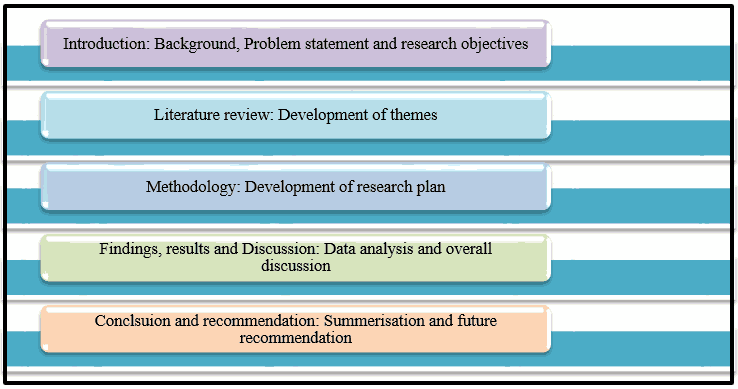
Figure 1.3: Structure of dissertation
(Source: Self-created)
1.8. Summary
The chapter has highlighted the areas of study for the research on the employee retention strategy of AHNAIZN Business Group. The research has been aimed at examining the strategies of employee retention, which have been employed by the firm to maintain organisational performance and employee satisfaction. The objectives and research questions have highlighted the areas of research. This research set out to investigate employee retention strategies, which can help UK businesses improve their strategies as well. Moreover, the chapter has included a problem statement, rationale, and the significance of the research along with a visual representation of the dissertation structure.
Chapter 2: Literature Review
2.1. Introduction
A literature review is the overview of a wide range of previously published work on a specific topic. The purpose of the literature review is to assess a segment of the published body of knowledge critically through classification, summarisation, and comparison of prior research papers. In this chapter, various prior research articles and journals have been used to analyse the employee retention strategy employed by the HRM department of AHNAIZN Group. It highlights various concepts related to HRM and employee retention strategy, conceptual framework, theoretical application, and literature gap.
2.2. Concepts
2.2.1. Purpose and the Importance of Human Resource Management
HRM is an essential process within an organisation, which plays a multifaceted role such as recruiting, managing, and overseeing management processes. According to Stahl et al. (2020), the primary objective of HRM is managing the workforce of an organisation. It plays a significant role in organisational success and growth. The HRM department of an organisation creates and enforces managing processes and methods, which allows the company to operate in terms of relations with its employees. These HRM rules help the firm’s stakeholders follow its primary goals and objectives. In addition, Chams and García-Blandón (2019) opined that HRM also makes sure that every individual follows the rules and regulations, which allows a firm to maintain fair operations. These rules and regulations include coordinating, planning, and directing various official tasks allowing an establishment to run a smooth organisational management process.
The authority of the company that is in charge of managing the HRM process is also known as the HR manager. The primary task of the HR manager is to monitor the recruitment and hiring of new employees. Wilton (2019) stated that these officials are also responsible for conducting freshers’ interviews and assessing their qualifications and documents. Further HR manager also takes care of the training and self-development process of newly hired employees. Most importantly Townley (2019) opined that HR managers are the bridge between the employees and the higher authority of the organisation, which plays a significant role in terms of making decisions. The primary purpose of practising effective HRM procedures is to maintain the workforce in a specific way, which can help the firm achieve its goals and build its unique culture.
Handling the HRM process effectively can provide an advantageous ground for companies to get new skills and expertise that can fulfil the company’s needs and help in the growth and development of existing employees. As per the understanding of Yong et al. (2020), a well-structured HRM process is significantly important for every organisation along with the effective HR manager, which can provide growth and success to the company. A well-structured HRM also focuses on talent management, as it plays a significant role in enhancing the entire HRM process. According to Statista (2023), approximately, 26% of companies have introduced talent management in their HRM process. It shows talent management’s significance as organisations acknowledge that nurturing and developing employees is a crucial part of organisational strategies. HRM also play a significant role in handling the post-emergency situation by implementing new strategies and plans.
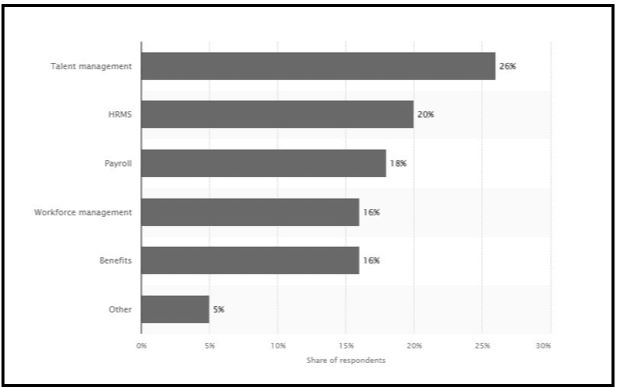
Figure 2.1: Application of HRM
(Source: Statista, 2023)
HR managers create and evaluate strategies to make sure that the employees are following the organisation’s objectives. According to Davidescu et al. (2020), they also contribute significantly to the decision-making process and accountability, which makes them responsible person for the organisation’s success and failure. Furthermore, assessing the skills and qualities of existing employees allows the HRM officials to understand the requirements for future needs. Townley (2019) stated that HR managers make recruitment processes to ensure that the newly hired employee can serve the company’s future purpose with their experience. The HR are also responsible people for listening and providing solutions to employees for the issue that occurs during organisational operations. According to Stahl et al. (2020), authorities related to the HRM process also focus on understanding employees and the way to make a better professional relationship between them. It helps to create a friendly and fair work atmosphere, where every individual is treated and respected equally.
2.2.2. Functions of HRM in various business organisations
HRM can be considered an engine, which helps organisations to maintain a smooth management process. This management process starts with developing the right rules and policies for the tasks of the company. According to Piwowar‐Sulej (2021), it further continues with ensuring that each task aligns with companies’ goals and development. HRM process connects all the elements of the firm and makes sure that the organisational process can run without interruption. Building an environment that can ensure that every stakeholder is doing their best and contributing towards the company’s success. As per the understanding of Suharti and Sugiarto (2020), it is not only about delivering tasks but also focusing on developing the skills and qualities of the workforce with time. The HR manager also helps to build leadership within an organisation by encouraging them.
Building leadership within an organisation requires a skilled workforce as they make fewer mistakes and are more efficient. Therefore, Identifying skills and qualities that can help an organisation to achieve success is a crucial part of the HRM system. According to Statista (2023), 53% of organisations have identified that the new capabilities and skills are essential in terms of the post-COVID-19 situation. However, 48% of HR professionals have considered developing remote working skills and 45% have considered exploring new ways to develop talents as HRM strategies. As per the understanding of Podgorodnichenko et al. (2020), HRM is not only about developing the skills of the existing workforce but also about finding skilled individuals for companies. Finding new skilled individuals significantly help an organisation to process new operation based on the company’s needs, as it barely requires further training or a development program.
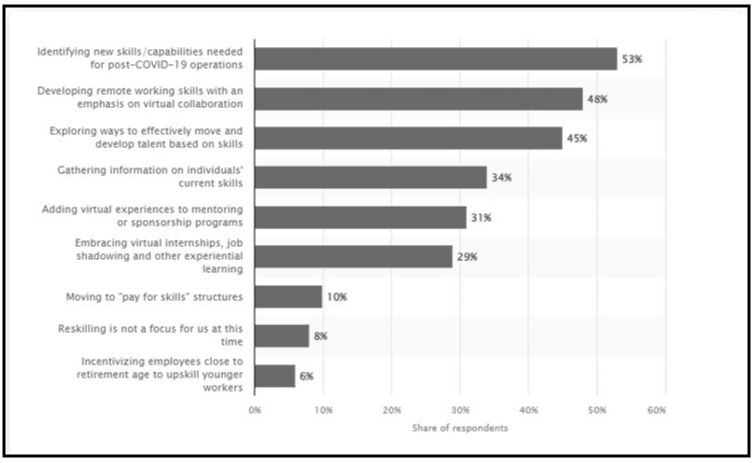
Figure 2.2: Functions of HRM
(Source: Statista, 2023)
The culture of a company makes it unique from others, where HRM play a crucial role in shaping the company’s culture. According to Sarvaiya et al. (2021), the process of recruiting, hiring, and training employees, can influence the culture of a company. The policy the company use in recruiting, hiring, and training creates the culture for every specific aspect. HRM also influence employees’ acts and attitudes through its rules and regulations, which shape the organisational culture. Shin et al. (2020) opined that an effective and sensible HRM process treats employees with dignity and respect, which not only affects employee behaviour but also shapes the company’s culture positively. On the other hand, an ineffective HRM process not only negatively affects the culture but also leads employees to dissatisfaction.
Other factors influence how HRM works, and one of them is cultural norms. As per the understanding of Suharti and Sugiarto (2020), it can be considered an unwritten rule in society, which decides how people are required to react to certain situations. Therefore, these cultural norms also affect the employees’ behaviours and having a similar organisational culture can provide a significant benefit to the firm in terms of better relationships with customers and suppliers. Shin et al. (2020)stated that in a simpler understanding, HRM is the process of managing and positively influencing employees’s surrounding environment. It allows the organisation to manage a positive culture and environment, which helps it to gain success and growth.
Moreover, by implementing these strategies and methods HRM can ensure that the organisation can grow and prosper while keeping stakeholders happy. Sarvaiya et al. (2021) stated that HRM helps employees become better at their jobs, which also allows them to work as a team. As HRM encourage people to work together, as a result, it develops a collaborative culture within the firm. Collaborative culture is one of the most essential aspects for business firms as it directly affects the work environment and employee engagement. Positive culture assists organisations in managing their diverse and large workforce smoothly, which contributes to higher efficiency and productivity. According to Podgorodnichenko et al. (2020), it is one of the most essential factors in facilitating positive employee retention plans as higher employee engagement often helps the HRM department of the business firms in easily managing their rate of employee turnover.
2.2.3. Essentiality of HRM in increasing CSR value of the firms
HRM is very important for organisations in terms of fulfilling “Corporate Social Responsibility or CSR”. CSR is the company’s responsibility towards the community, the environment, and its employees. In simpler terms, As per the understanding of Santana et al. (2020), CSR is not only about the responsibility of giving back to the community but also about doing good for the people. HRM play a crucial role in shaping an organisation’s commitment towards CSR by developing, understanding, and introducing strategies with good intentions towards society. Lee and Szkudlarek (2021) stated that the way the company considers its responsibility in society affects how HRM treats and directs employees. Once the company decides to contribute positively to society, its HRM process makes sure that the company’s employees are treated correctly.
It can be considered a ripple effect, where the company values social responsibility and it influences HRM to respect and care for employees connected. According to Meier et al. (2021), CSR is significantly important, as organisations have faced various changes in recent times. The business structure and the way it interacts with labour organisations, government agencies, and employees are changing in this globalised business world. These changes have increased the responsibility of organisations to focus on how they treat their employees. Franzoni et al. (2021) opined that fulfilling CSR is not only about the external appearance, it also includes internal approaches to how a company treat its employees and communities. Fulfilling CSR include treating the employee with respect, where HRM play a significant role. Treating employees rightly can be noticed in their improving mental and physical well-being.
In addition, CSR also influences employees’ and potential customers’ views about the organisation. As per the understanding of Sobhani et al. (2021), a company practising effective CSR can be a preferable place for both customers and employees. Job seekers value companies that encourage CSR within the organisation, as it creates a positive working environment. According to Santana et al. (2020), it develops an idea about the company that it is not only for making a profit but also for taking care of employees and communities. Therefore, enhancing the credibility of the company, HRM plays a crucial role in establishing CSR in all its operational practices. HRM make sure to keep the consistency of fulfilling CSR practices, which can help the firm treat employees well and make a positive reputation in the eyes of customers and potential employees.
Furthermore, a company’s commitment to CSR is driven by HRM. According to Meier et al. (2021), it respects workers’ rights, recognises the essence of “corporate social responsibility”, and adjusts to the dynamic nature of professional relationships. CSR is not merely an external representation for the public; it is an internal reflection of a company’s beliefs towards its workforce and the community. As per Franzoni et al. (2021), HRM often recruits younger workers who are environmentally conscious, which helps the firms to fulfil CSR. These workers are essentially enthusiastic towards CSR, which helps firms to develop a supportive culture within the organisation. It aids business firms in appropriately integrating innovative and creative ideas to reduce their carbon footprint in the global market. In this context, the employees understand the firm’s dedication toward environmental goals and community contribution, which also increases their engagement.
On the other hand, recruiting younger employees also allows companies to have new knowledge and expertise, which also helps HRM to utilise their ideas to enhance the CSR value of the firm. Employees’ enthusiasm creates a friendly competition environment, which helps HRM to fulfil CSR. The new generation is also conscious of green practices, which only makes the HRM effective in terms of implementing CSR. According to Lee and Szkudlarek (2021), CSR is another essential part of employee retention and recruitment strategy, which aids firms in improving their brand reputation in the global market. It enables them to attract suitable candidates, who are dedicated and maintain the existing workforce as well.
2.2.4. Influence of HRM on employee retention strategies
Keeping talented people has become a top priority for many organisations. It is believed that an experienced and highly skilled workforce is the key to organisational success and growth. As per the understanding of Islam et al. (2022), keeping experienced employees can provide various benefits to the organisation such as survival during critical situations, tackling unexpected challenges, and increasing profit. Finding and recruiting a workforce is important, however, keeping the existing skilled workforce is crucial, as it is where HRM play a significant role in employee retention. According to Papa et al. (2020), employee retention requires adapting various approaches including increasing wages, focusing on development, providing job satisfaction, and other employee-beneficial opportunities. Different organisations apply different approaches to increase employee retention rates through the effective HRM process.
One of the primary practice the HRM department do is to make sure that the workforce is providing its maximum efforts, which can ensure organisation growth and success. Malik et al. (2020), HRM keeps the tracking of potential employees’ performance and encourages them based on their efforts, which helps in employee retention. However, the primary concentration of the HRM process is to focus on the productivity of the whole company rather than focusing on individuals. According to Hassan (2022), the performance of teams depends on their expertise and the tasks they have been assigned by the HRM. Therefore, HRM pays close attention to aligning employees to their effective positions. Overall, the retention rate can be significantly influenced by the decision of the HRM process in terms of high performance and employment practices.
Another crucial factor that affects the employee working experience is workplace satisfaction. According to Islam et al. (2022), there is a very strong connection between how satisfied employees are in the workplace and how long they want to stay there. The company’s productivity, resilience, and efficiency can be boosted by the happiness of employees. Therefore, HRM plays a crucial role in eliminating wrong practices and biases in the workplace to enhance employee satisfaction. Hassan (2022) stated that HRM also plays an important role in developing a suitable work culture environment, where employees stay satisfied. It allows HRM to maintain workplace satisfaction among the workforce, which can positively affect the retention rate. Furthermore, a positive environment also increases the organisation’s productivity, which redirects to profitability.
Training and development a crucial factors in the HRM process, which influence employee retention. Papa et al. (2020) opined that employees appreciate having the chance to increase their capabilities, which can ensure their growth within the organisation. It is not only about getting a promotion but also increasing their skills and knowledge, which can help them in career development. According to Statista (2023), 50% of organisations have faced difficulties in the retention process due to the expectations for career development. HRM helps employees by providing various training and development programs, which not only increase the workforce skills but also the retention rate. Moreover, providing such programs can also help organisations to increase productivity along with the employee’s satisfaction. It also increases the employee’s engagement and gives them a reason to stay with the organisation.
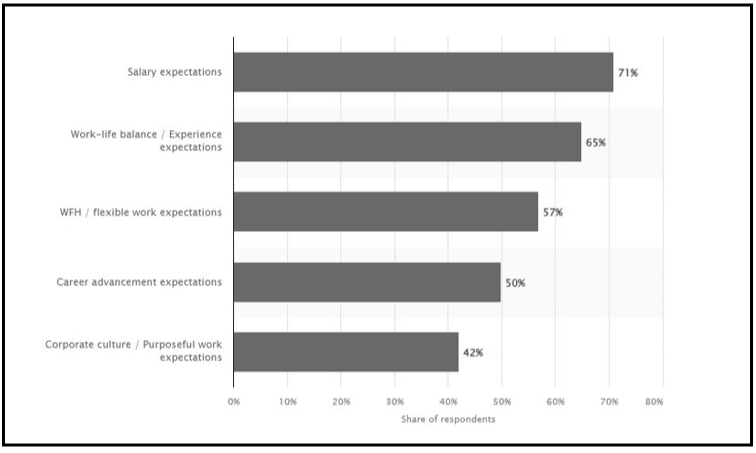
Figure 2.3: Factors associated with retention and recruitment challenges
(Source: Statista, 2023)
The work comes with the pressure of completing specific tasks with the given deadlines, which increases the mental pressure on employees. Therefore, according to Statista (2023), 57% of firms have faced difficulties in the retention process. Hence, HRM plays a significant role in providing flexibility in the work environment, which can increase retention rates.
2.3. Conceptual framework
Figure 2.4: Conceptual framework
(Source: Self-created)
2.4. Theoretical application
Organisational ecology theory
The organisational ecology theory, which was created by Hannan and Freeman, observes the changes in organisational population over time. It generally highlights five stages of population change, which are founding, growth, transformation, decline, and death. This framework also considers various economic, political, and social systems as well. The systems are generally associated with inducement in organisational diversity through the creation of a new organisational form and a decrease in organisational diversity, for instance, driving away certain organisational forms via competition (Vargas-Hernández et al. 2022). As a result, this theory looks at the dynamics of the organisational population, which can be highly effective for the HRM groups to analyse prior employee recruitment and retention policy to apply proper strategies for their respective firms.
Additionally, the theory of organisational ecology is segmented into three levels; the population, the organisation, and the community. The organisational level concentrates on individual organisations; whereas the population level focuses on the various organisations engaged in the same type of activities. On the other hand, the community level highlights the functionally “integrated system”, which consists of interacting populations (Öztürk and Esra 2022). Hence, the application of this framework can help in analysing the interaction between employees, organisations, and communities, which can assist in determining common patterns that help business organisations incorporate positive practices. As a result, the application of this theory can help business firms in analysing prior practices and interactions among people to recognise the challenges and facilitate appropriate practices.
2.5. Literature gap
The chapter has highlighted various concepts regarding HRM and factors related to employee retention. However, there is a significant gap in the study regarding the lack of evaluation of the role interns play in people’s function in AHNAIZN. Moreover, the study has highlighted the importance of HRM in the CSR activity of organisations. However, it has not been able to provide information specifically regarding managing conflicts in the workplace, which has a significant impact on employee retention. The importance of training and provide feedback to the employees to induce satisfaction and retention of employees has not been discussed. As a result, the research will address this gap in the literature in the later chapter of this dissertation.
2.6. Conclusion
The chapter sheds light on the various concepts related to HRM and their employee retention strategies and associated factors. An organisation’s HRM department develops and implements management procedures and policies, enabling the business to function in terms of its interactions with its workforce. The company’s stakeholders can better follow its main goals and objectives with the aid of these HRM regulations. Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) is a crucial component of employee retention and recruiting strategies that help businesses enhance their brand recognition in international markets. By using the organisational ecology framework, businesses can analyse how communities, organisations, and employees interact. This analysis can reveal common patterns that businesses can use to implement positive practices.
Chapter 3: Methodology
3.1. Introduction
Research Methodology offers detailed information about how the study was conducted. It offers a thorough methodology for the study to guarantee accurate and trustworthy findings that meet the goals and objectives of the investigation. The chosen research techniques, which are used to collect information on the employee retention techniques of HRM in AHNAIZN Business Group, have been explained and justified in this chapter. A few key concepts, methods, designs, decisions, data gathering, and analysis have been highlighted.
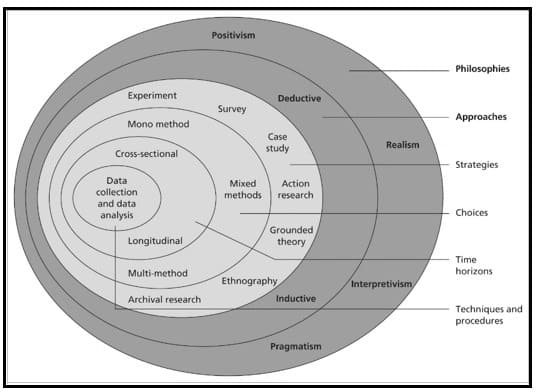
Figure 3.1: Research onion
(Source: Iovino and Tsitsianis, 2020)
3.2. Research philosophy
A research philosophy is a set of beliefs that emphasises an appropriate method for gathering information about a certain subject for study. It typically relates to gathering relevant information and selecting reliable data sources related to the study’s objectives (Mardiana, 2020). In general, research philosophy ensures that the study’s data collecting and evaluation procedures are integrated appropriately. Three primary categories of research philosophy can be distinguished: positivism, interpretivism, and realism. In general, positivism depends on factual information to provide sufficient context for understanding a particular occurrence. The use of positivism in research typically requires a sizable amount of data and helps obtain an unbiased perspective on an occurrence (Snyder, 2019). However, realism relies on scientific presumptions in order to understand a particular event. Nonetheless, a significant drawback of realism is its disregard for personal viewpoint. Conversely, interpretivism offers a comprehensive understanding and helps evaluate a phenomenon in light of society’s values.
In this research, positivism has been applied to analyse the employee retention techniques of AHNAIZN to analyse its effectiveness in the HRM department. Positivism informs that society and human behaviour are objective and can be quantified (Tayebi Abolhasani, 2019). Hence, the application of positivism has assisted in assessing the patterns and relationships between social factors, which has aided in analysing the appropriate process of developing the HR process in the organisation. Positivism has been useful in fostering knowledge of the HRM solutions needed by the organisation to enhance its business structure in the UK market. The positivist concept has aided in gaining a thorough understanding of the topic to determine the best course for organising the research (Newman and Gough, 2020). Adopting a positivist philosophy is a better approach to analyse human resource solutions and development criteria for employees of AHNAIZN Ltd. than realism or interpretivism as it relies on a scientific approach.
3.3. Research Approach
The term “research approach” refers to the methodology used in research that helps researchers collect and analyse data systematically. The three types of the research approach are the abductive, deductive, and inductive techniques. Research requires to investigate circumstances that are not yet understood, where the researcher uses the abductive approach (Vebrianto et al. 2020). The abductive research approach also allows the researcher to start the research with unusual and new elements in the research. The primary target of using this approach is to explain the surprising facts that have less information available. The deductive method allows the researcher to concentrate more on analysis because it takes less time to apply (Al-Ababneh, 2020). On the other hand, the efficacy of the inductive technique lies in its ability to gather and analyse data in scenarios when there is a lack of available information about the topic.
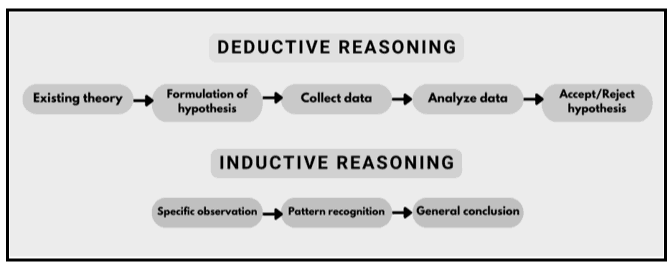
Figure 3.2: Comparison between inductive and deductive approach
(Source: Al-Ababneh, 2020)
This study has adopted a deductive method to assess how AHNAIZN Ltd., a UK-based company, uses HR solutions to increase employee retention and draw in new hires. Using pre-existing theories about the subject, the deductive approach aids in the analysis of the research (Djafar et al. 2021). In this study, analysing the effects of the employee satisfaction policies of AHNAIZN Ltd can be accomplished through the application of a deductive technique. The logical method has been justified in this situation. The deductive approach plays a significant role in providing an understanding of the variables in the research, which also helps researchers identify how they are connected and affect each other (Greening, 2019). It helps the researcher in using the result of the research in a wider way.
3.4. Research design
The method of conducting research that assists the researcher in determining what has to be accomplished and how to create the root map is known as the research design. in another way, the research design is a scientific framework that aids in the identification of methods and concepts for the particular study by the researcher (Willmott, 2020). It facilitates the growth and continuation of the root map research, which may enable the research to conclude. There are five different kinds of research designs; descriptive, experimental, correlational, diagnostic, and explanatory. These types of designs enable the conduct of research (Dodds and Hess, 2020). One popular kind of design that aids in the examination of the research variables and their interactions with one another is the “experimental” design.
Through manipulating a single variable, this research approach provides a deeper understanding of the effects of changes in one variable on other variables. In contrast, the “correlational” design encourages the observation of the link between several variables without changing the origin or cause of the variables. It enables researchers to comprehend the relationships and real-world reactions between many factors (Chivanga and Monyai, 2021). Once it comes to figuring out the underlying cause of a problem and coming up with solutions, the “diagnostic” design is incredibly beneficial. The study design uses a variety of strategies, including marketing to identify the areas that need improvement and have room for expansion. Once researchers face the crisis of limited availability of information, the explanatory design type is extremely helpful. Considering minimal data, the design type aids in understanding why a particular circumstance or problem arises.
The explanatory design concentrates on issues such as how and why it occurs. Descriptive research, on the other hand, aims to perform an organised process of analysing and characterising the subject’s behaviour without changing it. Since it enables the analysis of a situation through interviews, observation, polls, surveys, and case studies, the descriptive design is very crucial (Budianto, 2020). The utilisation of descriptive methods provides the researcher with a deeper knowledge regarding the situation by questioning the situation. This study, which aims to analyse the effects of HR solutions and policies to raise the employee retention rate at AHNAIZN Ltd., has chosen a descriptive design. An in-depth examination of the company’s HR policies and the way it may enhance its CSR policies to increase employee retention can be developed with the help of a descriptive research design.
3.4. Research Strategies
Research strategies are the plans or methods that facilitate the process of locating, gathering, and evaluating data related to an event. It typically has a greater impact on the research’s data collection procedure, which is chosen depending on the study’s goals, objectives, and time constraints (Delios et al. 2023). Grounded theory, action research, survey, experiment, case study, archival research, and grounded theory are its seven broad categories. While surveys can yield a significant quantity of data about an event, the experiment uses an empirical method to undertake in-depth research. In order to research the effects of different elements on each other, however, participants or the selected phenomenon are investigated and tested in a controlled environment during the experiment (Rumsey et al. 2022). Systematic research, which seeks to identify effective answers to common problems, is made easier by action research.
In order to address the issues that arise under certain circumstances, it takes into account the intricate details of society. However, one of the most popular kinds of research in industrial marketing is the case study, which examines a variety of case studies that are accessible regarding a particular occurrence (Dzwigol, 2022). Because grounded theory is based on qualitative approaches, it can be developed more easily than theories that rely on methodical data collection and evaluation. In addition to that, ethnography refers to the complex social research conducted through various processes such as interviews, observations, and more. Archival research uses journals, articles, and historical archives to determine the gap in the existing research.
The case study and the survey approach have been chosen as the research strategy in this study in order to highlight the employee retention strategy of AHNAIZN to analyse the importance of HRM and its functionalities. The survey process has assisted in gaining quantitative information regarding the research (Acampora et al. 2022). The case study approach has helped to examine and analyse the influence of HRM in creating an effective employee retention strategy. The utilisation of the case study approach has facilitated the acquisition of a broad and thorough understanding of the employee retention strategy of AHNAIZN Business Group and the role of the HRM department in maintaining employee turnover.
3.5. Research Choices
The kinds of data used in the research process are determined by research decisions. There are three main categories of research choices: single, multi, and mixed-method. The method used for data collecting and analysis in a study is greatly influenced by the sort of research option chosen (Babii, 2020). It depends on the kind of data both qualitative and quantitative that needs to be gathered for the study. The mono approach emphasises using just one kind of data, qualitative or quantitative for a given study. The process of utilising both qualitative and quantitative methods to fully comprehend the study issue is highlighted by the mixed method (Ryder et al. 2020). Conversely, multi-methods typically employ more than two approaches to obtain pertinent data for the study. Multi-method research includes, for example, the use of content and theme analysis in addition to quantitative data collection.
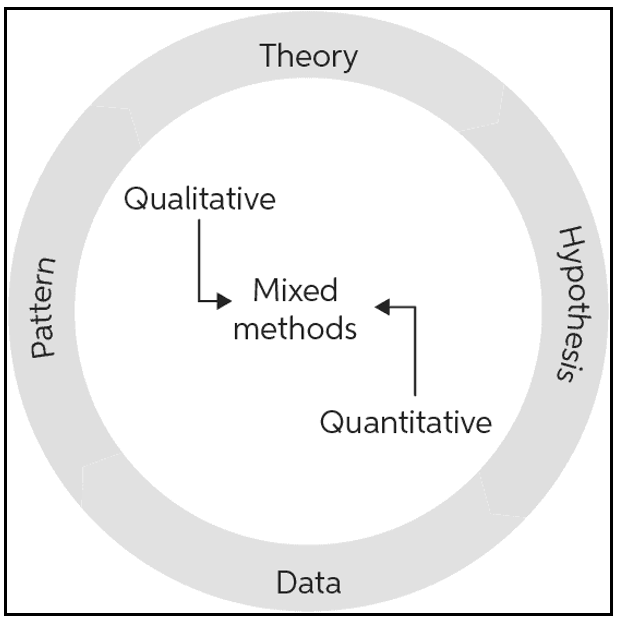
Figure 3.3: Mixed method
(Source: Babii, 2020)
Comparing mono and mixed processes to multi and mixed processes, the mono technique takes less time because it uses just one type of data collecting. In this research, the mixed method has been integrated into the research to utilise qualitative and quantitative data in the study. The qualitative data has been collected through the secondary method and the quantitative information has been gathered through the survey process to analyse the employee retention strategy of AHNAIZN Business Group.
3.6. Time Horizon
The term “time horizon” refers to the study timetable, which often guides the duration and frequency of data gathering related to a certain subject or event. The frequency of data collection at different times during the investigation is determined by the time horizon (Urcia, 2021). The two primary categories of temporal frames are cross-sectional and longitudinal. Researchers can gather data for longitudinal studies at different intervals in time, enabling them to compare changes and spot new patterns. Because data is gathered repeatedly, the longitudinal approach consequently usually lengthens the data-gathering procedure (Sileyew, 2019). Conversely, cross-sectional investigations necessitate collecting pertinent data only once. As a result, it takes a lot less time than the longitudinal method.
The present study has used a cross-sectional technique to investigate the employee retention process of the HR department of AHNAIZN Business Group. It has made the process of gathering data more efficient by facilitating the quicker gathering of pertinent information about the study. As a result, the cross-sectional method has helped to shorten the time needed to collect data.
3.7. Sampling Techniques
Across a broader population, the practice of gathering data from a specific group of people is referred to as sampling procedures. There are two categories of sampling techniques: “non-probability sampling” and “probability sampling.” The information-gathering technique known as “non-probability sampling” involves selecting samples based on non-random criteria (Patel and Patel, 2019). This sampling technique is riskier in terms of sampling bias because it is simpler and less expensive. However, the probability sampling approach lets everyone take part in the data collection, which enables a researcher to obtain a wealth of information about a particular occurrence (Urcia, 2021). Since “quantitative research” is the main application for probability sampling, it is very beneficial when gathering data from a bigger population. There are four categories of sampling in the probability method: cluster sampling, systematic sampling, stratified sampling, and “simple random”. Cluster sampling is a technique for gathering data that involves breaking down a big population into smaller groups.
The procedure of giving each person a unique number enables the sampling technique to gather data from people regularly and is known as systematic sampling. A big population can be divided into smaller groups using stratified sampling, which makes it easier for researchers to make sure the data from those groups are accurately represented in the sample (Acampora et al. 2022). In this study, the simple random approach has been chosen to collect secondary data in order to determine the impact of HR policies and solutions on increasing AHNAIZN Ltd.’s employee retention rate. It is possible to select every member of the population using a basic random sampling technique. Additionally, survey participants in the research have been chosen from among those who have worked in or are currently employed by the AHNAIZN Business group.
3.8. Data collection
The process of gathering information on a certain event or study topic is known as data collection. There are two forms of data collection: primary and secondary, depending on the method used. During the first step of the research process, pertinent data is typically gathered by interacting with respondents through surveys, interviews, and polls (Rumsey et al. 2022). Conversely, the secondary procedure gathers journals, publications, and previous research papers to use data from the body of existing research. Secondary data collection takes less time than initial data collection. Furthermore, the data-gathering procedure can be further separated into two categories: qualitative and quantitative, based on the type of data (Willmott, 2020). Qualitative data is often informative in nature and can be obtained by gathering data from secondary sources or by conducting interviews.
Conversely, quantitative data is gathered through polls, surveys, and the collection of statistical data from many sources. This research has utilised primary quantitative and secondary qualitative methods to collect information regarding the employee retention strategy of AHNAIZN. The secondary qualitative information has been gathered from ProQuest and Google Scholar to obtain related articles, research papers, journals, and more (Vebrianto et al. 2020). The primary quantitative data has been collected by conducting a survey of 30 respondents. Data from the research survey and secondary data from research papers have been gathered for this study in order to assess the company’s current standing in the business market and determine whether staff retention policies are necessary to mould the organisational structure.
3.9. Data analysis
The process of evaluating and scrutinising the gathered data in order to address the research questions is known as data analysis. There are two categories of data analysis: primary and secondary (Mardiana, 2020). The research regarding the employee retention strategy of HRM of AHNAIZN has used both primary quantitative and secondary qualitative information. In order to include the evaluation of the survey results in the specification of the company objectives, a graphical representation of the survey responses has been included. The approach of thematic analysis has been integrated to analyse the secondary information, which has increased flexibility and brought to light a number of patterns pertaining to employee retention approaches.
3.10. Inclusion and exclusion criteria
The factors that are maintained throughout the data collection process are highlighted in the “inclusion and exclusion criteria”. Older literature sources that were released prior to 2019 were not included in this study. Furthermore, sources that are accessible in languages other than English are not included in the analysis. Conversely, the research’s inclusion criteria include sources that are published between 2019 and 2023 and are accessible in English. Additionally, respondents, who have worked in or still working in the AHNAIZN Business group have been selected as survey participants in the research.
3.11. Ethical considerations
Research ethics is a crucial component that supports the upholding of ethical standards. The study rigorously prohibits plagiarism, and all of the research materials that were gathered have been correctly cited. The research has adhered to the “Privacy Data Protection Act of 2018” when gathering both primary and secondary information from sources. The primary data and information gathered from participants have been kept private by the researcher (Greening, 2019). The participants have been informed regarding the purpose of the study to gain informed consent. Furthermore, reliable and legitimate data have been gathered for the study through the usage of sources like Google Scholar and Proquest.
Figure 3.4: Ethical considerations
(Source: Greening, 2019)
3.12. Conclusion
The chapter has provided insight into a thorough research process planning to assess the employee retention strategies of HRM of AHNAIZN. The mixed approach was used in this research to incorporate both qualitative and quantitative data into the study. The primary quantitative data has been collected from 30 employees of the organisation through conducting a survey. The respondents have been informed regarding the purpose of the study to obtain informed consent.
Chapter 4: Findings and Discussion
4.1. Introduction
The findings and discussion have provided an in-depth analysis of the survey results and a thematic analysis of the secondary data to facilitate a discussion regarding the effectiveness of HRM in employee retention.
4.2. Findings from the survey
Gender
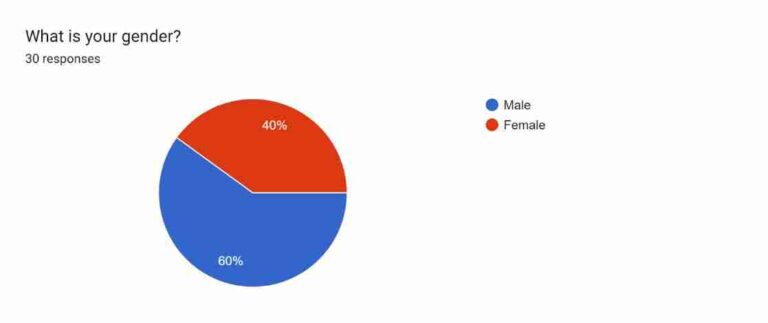
Figure 4.1: Gender
(Source: Self-created)
The first demographic question is regarding the gender of the respondents. Around 40% of respondents are female. On the other hand, 60% of respondents are male. It highlights that the survey has recorded a higher number of male participants.
Age
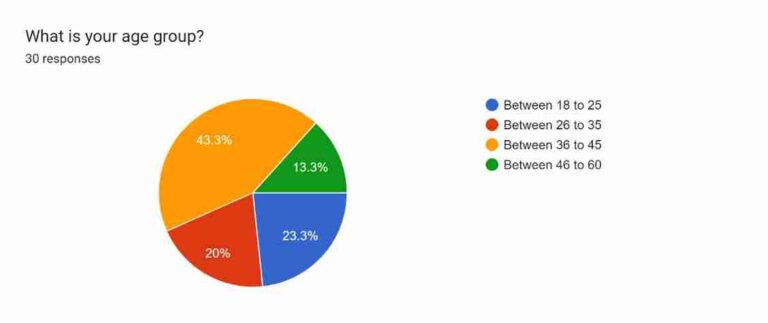
Figure 4.2: Age
(Source: Self-created)
The second demographic question is regarding the age of the participants in the survey. There are four options provided for the choosing age: “Between 18 to 25”, “Between 26 to 35”, “Between 36 to 45”, and “Between 46 to 60”. Around 43.3% of the participants belong to the age group of “36-45 years”. On the other hand, the age group of 46-60 years has recorded the lowest response with 13.3%. The age group 18-25 years has 23.3% responses, whereas the 26-35 years age group has obtained 20% responses in the survey. As a result, it can be said that individuals between 36-45 years have shown increased interest in the survey regarding the employee retention strategy of HRM.
Work experience
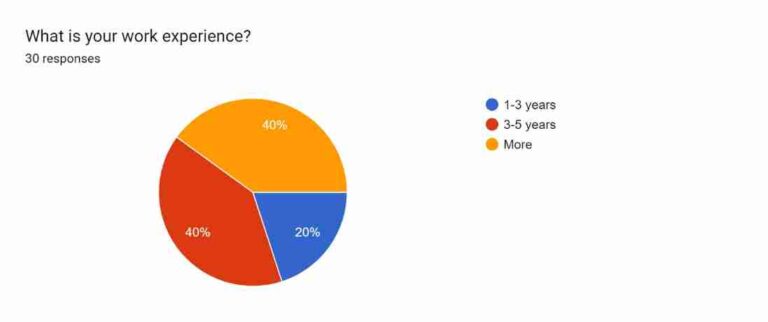
Figure 4.3: Work experience
(Source: Self-created)
The third and last demographic question is related to the work experience of the respondents. Around 20% of participants have work experience between 1 and 3 years. On the other hand, participants with 3-5 years of work experience recorded 40% responses in the survey. Similarly, individuals with more than 5 years of work experience recorded 40% of the responses. Hence, it is evident that individuals with 3-5 years and more work experience have shown higher involvement in the survey process.
Organisational goals and work environment
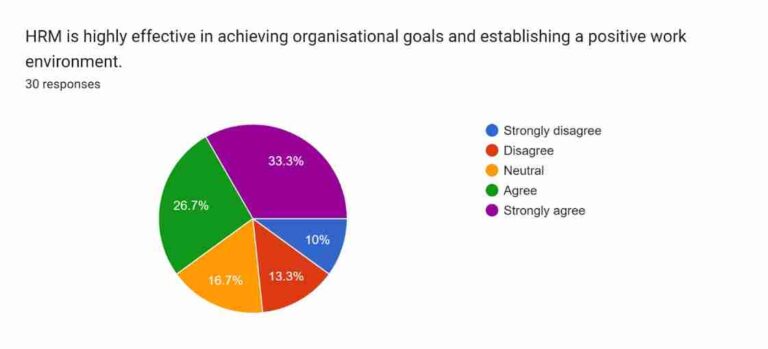
Figure 4.4: Organisational goals and work environment
(Source: Self-created)
The fourth question is regarding the effectiveness of HRM in creating a positive work environment and achieving organisational goals. The question has been provided with multiple choices: “Strongly disagree”, “Disagree”, “Neutral”, “Agree”, and “Strongly agree”. Approximately 33.3% of participants strongly agreed that HRM is essential in maintaining a positive work atmosphere and helps in obtaining organisational goals. 26.7% of the participants agreed with the notion of the effectiveness of HRM. However, 16.7% of the respondents have remained neutral. Around 13.3% of the participants disagreed with the effectiveness of HRM regarding the work environment and achieving organisational goals. Moreover, 10% of the respondents strongly disagreed with the essentiality of HRM in this matter. The number of participants, who have agreed to the effectiveness of HRM is relatively high, which indicates that the majority of the individuals recognise the importance of HRM in business organisations due to their involvement in aligning with organisational goals and creating an adequate environment for all employees.
Corporate Social Responsibility initiatives
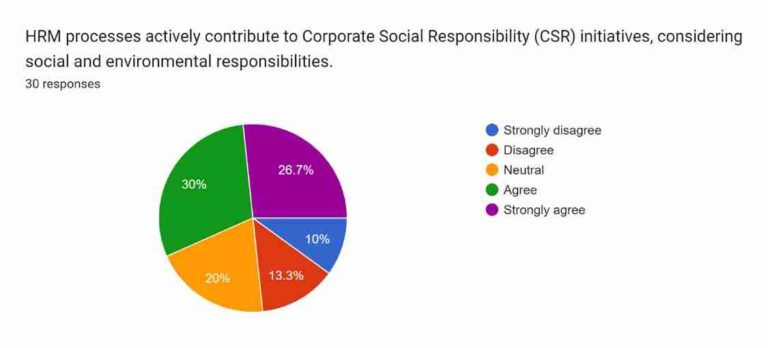
Figure 4.5: Corporate Social Responsibility Initiatives
(Source: Self-created)
The fifth question focuses on the contribution of HRM in terms of fulfilling CSR initiatives including social and environmental responsibilities. Around 26.7% of the participants in the survey strongly agree that HRM has contributed to fulfilling CSR and almost 30% have acknowledged that CSR initiatives regarding social and environmental is the responsibility of HRM. HRM focuses on green initiatives and sustainability, community engagement and helping, and employee well-being and work-life balance (Ababneh, 2021). The participants have stayed neutral around 20% in this survey. However, around 13.3% of individuals disagree with the concept of the contribution of HRM in CSR and approximately 10% of participants strongly disagree with the contribution of HRM in CSR. The survey highlighted a majority of the population agreed with the contribution of HRM in terms of fulfilling social and environmental responsibilities. Therefore, it proves that HRM plays a significant role in successfully fulfilling corporate social responsibility.
Alignment of organisational strategies

Figure 4.6: Alignment of organisational strategies
(Source: Self-created)
The sixth question explores the opinion of the participants of the survey process regarding the role of HRM in aligning CSR with organisational strategies, which assists in facilitating a positive impact on the community and society. CSR initiatives are generally targeted to provide the local community with long-term benefits and to reduce the environmental impact of a business (Kong et al. 2020). Around 33.3% and 26.7% of the respondents strongly agreed and agreed to the role of HRM in synchronising organisational strategies with CSR initiatives. Around 13.3% of the respondents have remained neutral in this instance. On the other hand, 16.7% and 10% of survey respondents have chosen to disagree and strongly disagree with the statement. The majority of the respondents have asserted a positive toward the role of HRM in aligning CSR initiatives with organisational strategies, indicating their active involvement in the process.
Positive work environment
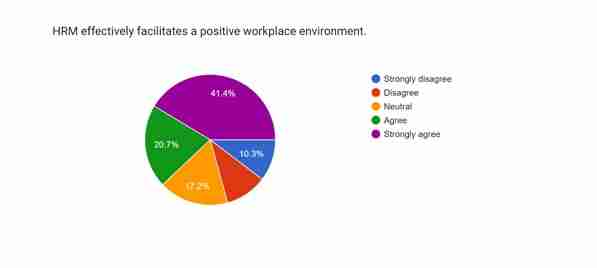
Figure 4.7: Positive work environment
(Source: Self-created)
The seventh survey question states that HRM is highly effective in facilitating a positive environment at the workplace. Around 41.4% of the respondents strongly agreed with the statement informing involvement of the HRM is creating an affirmative work atmosphere. HRM generally implements various rules and regulations to create an inclusive environment for a diverse workforce, which in turn increases the overall performance of firms (Podgorodnichenko et al. 2020). Nearly 20.7% of the participants also agreed with the statement. However, 17.2% of the respondents have chosen neutral as their option, which indicates they somewhat agreed with the involvement of HRM in creating a positive work environment. On the contrary, the strongly disagree and disagree option has been recorded in 10.3% of responses indicating only a small number of participants do not identify the role of HRM in establishing a positive work atmosphere. Analysing the responses recorded in the survey, it can be said that HRM plays a significant role in creating an adequate work environment for all employees.
Workplace concerns
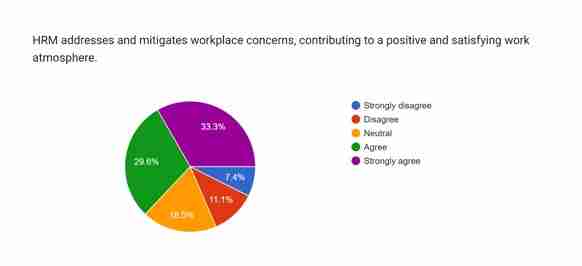
Figure 4.8: Workplace concerns
(Source: Self-created)
The eighth question has queried the role of HRM in addressing and resolving various workplace concerns to establish a satisfying work environment. Approximately 33.3% of the respondents strongly agree to inform active involvement of the HRM in resolving workplace conflicts. Additionally, 29.5% of respondents have agreed to the effectiveness of HRM in addressing and solving workplace concerns, which helps in creating a satisfying atmosphere at work. HRM usually analyses the challenges the employees are facing in the workplace to create new regulations to mitigate workplace concerns (Rajput et al. 2023). Nearly 18.5% of participants have remained neutral in this instance. On the other hand, 11.1% and 7.4% of the participants have chosen “disagree” and “strongly disagree” to inform their opinion regarding the effectiveness of HRM in managing workplace concerns. As the survey has received a relatively small number of responses against the statement regarding the effectiveness of HRM in solving workplace concerns, it highlights the essentiality of HRM in this matter.
Talent management
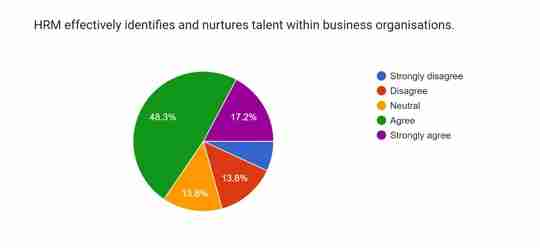
Figure 4.9: Talent management
(Source: Self-created)
The ninth question focuses on the effectiveness of HRM in identifying and nurturing talent within business establishments. Around 6.9% of participants in this survey strongly disagree that HRM has any contribution to identifying and nurturing talent within a company. However, almost 17.2% have acknowledged that HRM effectively identified talent and nurtured them in a company. Throughout the processes of workforce planning, recruitment and selection, onboarding and integration process HRM identify and nurtures talent within an organisation (Lee and Szkudlarek, 2021). Notably, almost 48.3% have significantly supported the claim that HRM plays a crucial role in marking and growing talent within business establishments. On the other hand, around 13.8% chose to stay neutral in this survey and did not provide any specific viewpoints. Similarly, approximately 13.8% disagreed with the contribution of HRM in terms of identifying and nurturing talent in businesses.
Well-structured talent management process
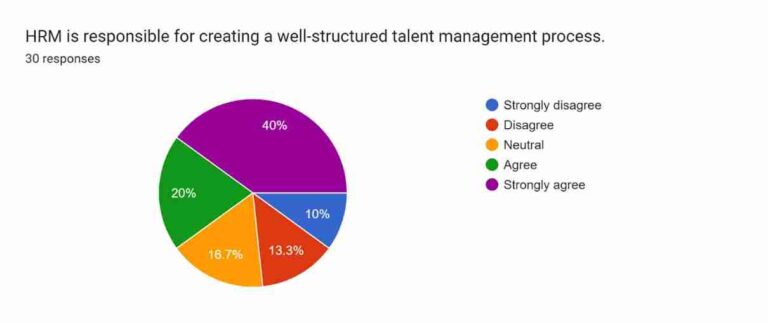
Figure 4.10: Well-structured talent management process
(Source: Self-created)
The last and tenth question is regarding the responsibility of HRM in establishing a talent management process. The talent management process generally includes recruiting, training, and retaining talented employees (Kravariti and Johnston, 2020). Around 40% of the participants strongly agreed and 20% of the participants agreed with the statement. Therefore, a total of 60% of the participants asserted that HRM is highly effective in incorporating a well-structured talent management process. Around 16.7% of the respondents have remained neutral in this instance. On the contrary, 13.3% and 10% of the participants have chosen to disagree and strongly disagree indicating that they do not agree with the role of HRM in creating a proper talent management process. This question recorded around 60% of respondents, agreed with the contribution of HRM in the talent management process indicating its essentiality in the business firms to manage their employees.
4.3. Findings from secondary data
4.3.1. Theme 1: Role of HRM in establishing a positive organisational culture
Recruitment and selection are crucial in the entire HRM process, contributing to building a positive organisational culture. During the process HRM professionals not only focus on people with skills and expertise but also on their culture that can fit with the company (Botelho, 2020). HR professionals also conduct behavioural interviews, which inform them about a person’s behaviour and the possibility of suiting with the organisation. HRM department also focuses on conducting training modules to focus on the fundamental principles and actions that help shape the positive culture within an organisation. HRM invest in training programs that ensure the enhancement of communication skills within the organisation, which not only helps to build good relationships among employees but also builds a positive culture (Roscoe et al. 2019). It includes active listening training constructive feedback, and communication channels.
HRM are also responsible for listening to the concerns and suggestions of employees, which encourages them to establish feedback mechanisms. HR officials provide regular pulse surveys or suggestion boxes to collect information that employees want to provide, which not only helps to increase employee engagement but also builds a positive organisational culture where everyone is heard (Al-Swidi et al. 2021). In addition to that, the HR department facilitates a performance-based recruitment system to hire employees from diverse cultures. Employees provide crucial and critical information regarding the organisation, which helps in mitigating challenges that the workforce faces. HRM also collaborate with organisational leaders to define their key leadership qualities and responsibilities, which can align the leaders with the organisation’s vision. An engaged leader not only helps the firm achieve its success but also encourages employees to connect with the company’s vision.
4.3.2: Theme 2: Importance of HRM in conflict management
There are various conflicts can exist within an organisation such as interpersonal and intragroup conflict caused by differences in personalities, and communication styles of individuals or groups, task conflict, process conflict and role conflict. HRM plays a significant role in identifying, addressing, and implementing solutions in the conflict management process, which minimises negative effects and promotes positive outcomes (Nash and Hann, 2020). The survey and feedback that are collected from employees in the HRM process, allows the HRM professional to identify conflicts at an early stage. It allows them to address the issue accordingly and invest resources in terms of the necessary situation to eliminate the cause of conflict.
HRM departments are responsible for developing and implementing clear conflict resolution policies, which ensure that all kinds of conflicts need to be addressed from a neutral perspective. It not only builds a positive culture in the organisation but also ensures that all conflicts are handled in a fair manner (John-Eke and Akintokunbo, 2020). Similarly, HRM also plays the role of mediator with a neutral perspective, it allows them to understand the concerns of all sides and provide resolution to mitigate challenges that are causing the conflicts. HR professionals are responsible for designing and providing conflict resolution training to employees, which develops understanding capabilities within the workforce to address conflicts (Rahim and Katz, 2020). Furthermore, the efforts HRM makes in developing an open communication culture also minimises conflict by sharing and understanding the concerns, perspectives, and needs of each other.
4.3.3: Theme 3: Essentiality of HRM in providing feedback
The organisation works in a complex structure and the role of HRM is significantly important, especially in terms of providing feedback. The process of maintaining a professional relationship is not only about exchanging information but also a strategic tool, which helps both the company and its people to come together and align their goals (Chong et al. 2020). The feedback system contributes more than just providing performance numbers, it ensures that a positive relationship can be built between the workforce and organisation goals. The feedback process also can be considered as a conductor that ensures a strong alignment between the employee and the organisational objectives (Eva et al. 2019). In simpler terms, the feedback process is significantly important for various aspects of organizational health. Most importantly, it promotes a culture of always getting better and creating an environment within the organisation, where helpful feedback is not just accepted by employees but also actively encouraged.
Throughout these processes, HRM takes on the responsibility of creating an ongoing conversation among the workforce and higher officials of the establishment. Effectively implementing a positive feedback system turns into teamwork and pushes both individuals towards collective progress. HRM also plays a crucial role in achieving growth for personnel by providing customised and valuable information (Burnett and Lisk, 2021). This strategic way of providing information not only helps in improving individual skills but also enhances the overall abilities of the workforce, making the organisation more robust. Therefore, the feedback process can be considered as a joint effort for shared growth and success.
4.3.4: Theme 4: Process of HRM in maintaining staff fulfilment
The process of HRM plays a crucial role in terms of developing an environment within an organisation, where employees find fulfilment in their work. The satisfaction and engagement of the workforce are significantly important for organisational success and HRM remarkably contributes to this target (Mira et al. 2019). The HRM departments use technologies to increase their efficiency in making decisions by analysing and understanding data. The utilisation of technology allows platforms where employees can help themselves, making their experience in the organisation better. Employee fulfilment directly contributes to their satisfaction, which leads to an increased retention rate. Therefore, HRM uses an exit interview process, where a meeting is conducted between the employee who leaving a job and a representative of the organisation.
Getting feedback and information from the employee who is leaving the job allows HRM officials to understand the reason for dissatisfaction and addressing that issue allows them to fulfilment of existing employees (Anbu, 2019). HRM also focuses on creating a workplace with people from diverse backgrounds, which allows different people to work in an inclusive culture. Establishing rules and policies to ensure that every employee gets equal chances and is treated respectfully shows that HRM values different viewpoints, which creates a happy work environment and ensures employees’ fulfilment. HRM also focuses on addressing conflict by dealing with issues and disagreements among employees (Inoyatova, 2021). It involves taking openly, finding resolutions to concerns, and implementing solutions strategically, which not only helps HRM departments maintain a positive culture within the firm but also ensures employee fulfilment.
4.4. Discussion
HRM plays a significant role in managing employee retention in business firms. Managing conflicts in critical situations is one of the most vital aspects of managing employee satisfaction in the workplace. Conflicts generally occur due to varied perspectives of the employees in adverse situations, which can lead to bigger challenges in case they are not handled effectively (Anbu, 2019). HRM plays a significant role in maintaining and building a positive work environment within a business organisation. Later on in the survey, it was identified that a large population of around 41.4% of people strongly agreed that HRM effectively facilitates a positive work environment, which also contributes to building a positive organisational culture. Considering the disagreement population, which is around 10.3%. Therefore, the survey results align with the outcome of the secondary analysis, which informs that HRM has a significant contribution to creating a positive work culture.
Existing conflicts between team members can hinder the work progress and negatively affect the work environment. In order to avoid conflicts, the HRM department can provide the employees with various training programs to manage anger and awareness to provide effective tools and resources to the employees (Al-Swidi et al. 2021). It can help them in analysing the situation and assist them in managing their emotions adequately in the workplace. It can lead to better decision-making and collaboration among the workers facilitating higher productivity. Conflict management is a crucial responsibility in the HRM process. The process of conflict management involves focusing on communication channels, individuals’ behaviour, and task conflicts.
The result received from the survey of workplace concerns, shows around 33.3% of the population strongly agree that HRM plays a significant role in addressing and mitigating workplace concerns and only 7.4% strongly disagree with a similar claim. Hence, the secondary survey result confirms that HRM has a crucial part in conflict management. On the other hand, there are many ways HR managers can maintain employee satisfaction in the work process. The HR department needs to establish a proper communication channel with the employees to provide them with constructive feedback based on their performance. Effective feedback and guidance help the employees to increase their efforts and identify their areas of weakness (Chong et al. 2020). It can induce employee motivation toward self-regulation to improve their drawbacks, which provides a sense of purpose. As a result, it can create a positive environment in the workplace and motivate employees to improve their productivity at the workplace.
Additionally, the collected data from the survey process has highlighted the effectiveness of providing feedback to the employees in reducing higher employee turnover. Providing feedback is a crucial part of HRM, which can be considered an organisational goal that helps to build a positive work environment (Eva et al. 2019). Helping employees to enhance their capabilities by providing feedback is a significant organisational goal, which helps to build a work culture that promotes sharing information. The survey of organisational goals and work environment shows strong support with approximately 33.3%, which highlights the essentiality of HRM in maintaining a positive workplace culture.
4.5. Conclusion
The chapter has shed light on the outcome of the survey and secondary data analysis process, which has indicated the essentiality of HRM in employee retention. The discussion has linked the survey results with the outcome of the thematic analysis of secondary data. HRM has been emerge as an essential factor in managing employee retention process through maintain positive environment, adequate culture, providing feedback, and establishing positive culture. The results of the survey has been presented through pie chart to provide a visual representation of the recorded responses.
Chapter 5: Conclusion
5.1. Conclusion
In corporate organisations, HRM is crucial to controlling staff retention. Controlling conflicts in high-stakes scenarios is one of the most important components of controlling worker satisfaction at work. Conflicts typically arise from different points of view held by employees in difficult circumstances, and in case, they are not resolved well, they may escalate into more serious issues. Team disagreements can impede productivity and have a detrimental impact on the workplace atmosphere. The HRM department can offer the staff a variety of anger management and awareness training programmes to help prevent conflicts by giving them useful skills and resources. It can aid in assessing the situation and help them effectively control their emotions at work. Improved decision-making and increased teamwork among employees can result in increased production.
However, HR managers have a variety of options for preserving worker satisfaction throughout the working environment. In order to provide employees constructive criticism based on their work, the HR department needs to set up a good line of communication with them (Dalessandro and Lovell, 2023). Employees can pinpoint their areas of weakness and step up their efforts with the support of constructive criticism and direction. Employee motivation towards self-regulation to address their shortcomings may be induced, giving them a sense of purpose. It can therefore inspire workers to increase their productivity at work and foster a positive work environment (El-Sharkawy et al. 2023). Furthermore, the data gathered from the survey procedure has demonstrated how beneficial it is to give employees feedback in order to lower employee turnover.
The research has provided a comprehensive view regarding various employee retention strategies of HRM. It has evaluated the essentiality of HRM in managing employee performance and behaviour in the workplace along with conflict management. Additionally, establishing appropriate communication to provide frequent feedback to the employee has emerged as one of the suitable approaches to facilitate employee retention (Gelencsér et al. 2023). Moreover, providing employees with training processes to manage anger, understanding diverse cultures, and providing employees with adequate knowledge and resources can help in reducing conflicts (Mahdy et al. 2023). As a result, this research can be highly beneficial for small and medium-sized organisation to improve their employee management process to facilitate appropriate retention process.
5.2. Linking with objectives
Linking with Objective 1
The first objective is to elaborate on an HR intern’s role in developing people’s function in an organisation. An HR intern plays a significant role in employee management and engagement within a company. HR interns take active participation in the employee recruitment and selection process, which allows them to understand the candidates’ culture and helps to align it with the culture of the organisation (Mahdy et al. 2023). It allows all employees to connect with each other and increase employee engagement. HR interns also work as an active element in the HRM process, which allows them to identify and address conflicts by engaging in conflict resolution processes. The role they play in the exit interview is also crucial to understanding the problem in the organisation, addressing issues and building employee engagement with the company.
Interns also help to create a culture of continuous improvement by providing feedback from their unique perspectives and assumptions. HR interns utilise technologies to enhance the HRM process, which helps them with inefficient decision-making (Mohamed Husni and Jais, 2023). The incorporation of feedback mechanisms and technologies provides vast information about the firm to HR interns. It not only increases the effectiveness of overall HRM processes but also the people function.
Linking with Objective 2
The second objective covers the CSR activities and organisational performances that can contribute to the firm’s employee satisfaction. CSR activities such as developing a working environment with individuals from diverse backgrounds can contribute to an inclusive culture. Allowing and encouraging diverse groups of people to work together significantly increases employee satisfaction (Okojie et al. 2023). Creating a positive organisational culture by collaborating organisation leaders with the HRM process enhances leadership qualities by handling employees sophisticatedly and increasing the satisfaction of employees. CSR activities encourage diversity and inclusion within a workforce, which helps to mitigate conflict by creating a respectful work environment.
Addressing conflicts strategically and openly that align with the CSR principles helps to promote a positive organisational culture, which enhances employee satisfaction. CSR activities encourage an open communication culture that aligns with the role of HRM and builds conversations and feedback mechanisms. Communicating openly with outside communities provide benefit to the communities including employees’ friend and families, which increase the satisfaction of the workforce (Škerháková et al. 2022). CSR activities, such as incorporating technology to increase efficiency in decision-making, contribute to organisational performance and enhance employee satisfaction. Overall, CSR activities and organisational performance serve as a foundation for providing opportunities to enhance employee satisfaction.
Linking with Objective 3
The third objective analyses the process of recruitment of interns in the AHNAIZN Business Group followed by the HRM process of the company. The recruitment process of AHNAIZN not only values technical skills but also the individual’s cultural aspect, which can be aligned with the organization. Behavioural interviews play a significant role in AHNAIZN’s understanding of participants’ cultural compatibility with the firm (Tej et al. 2021). The interview ensures that an employee is culturally fit for the organisation and also helps them to participate in conflict prevention practises. AHNAIZN generally conducts physical interviews, which allows the officials of HRM to interact with participants directly and allows them to understand their compatibility with the establishment.
The recruitment process also involves real-time conversations with the participant, which allows the HRM professional to provide feedback regarding their interview. The officials of AHNAIZN also take feedback from the participants of the interview, which allows the company to identify the gaps in their interview process and contribute to overall HRM (Xiang et al. 2023). Furthermore, the HR department of AHNAIZN hires people based on their performance by using a system that focuses on how well participants can be aligned with the organisation.
Linking with Objective 4
The fourth objective focuses on how AHNAIZN Business Group contribute to the inclusion of new employees. The organisational culture at AHNAIZN plays an important role in welcoming and integrating new employees into the organisation by ensuring that the culture of new employees can be aligned with the company. AHNAIZN promote a culture where people from different background and beliefs are welcome, which allows the HRM department to include a diverse group of people in their operational team (Mohamed Husni and Jais, 2023). The diversity and inclusion culture of the firm significantly reduces the conflict among the workforce, which helps new employees connect with the organisation. It allows the employees to prevent conflict as they respect each other, therefore, AHNAIZN is able to incorporate new employees from different backgrounds.
The firm open communication culture allows the employees to provide feedback regarding their concerns and issues related to the organisation. It helps AHNAIZN to incorporate employees with different perspectives as they have the assurance that employees can be aligned with the organisation by sharing concerts (Ma Janice et al. 2023). Incorporating technologies in the recruiting process helps AHNAIZN to reduce bias in the process, which promotes an inclusive culture from the beginning.
5.3. Recommendations
The HRM department of the business firms needs to provide the employees with effective career and personal development initiatives to retain employees more efficiently. Career development plans generally provide workers with a scope to plan their future objectives. It motivates them to improve their skills and knowledge to gain promotion and additional benefits within the organisation (Ghani et al. 2022). Scope for career improvement reduces the rate of employee turnover, which assists the HRM department in retaining talented employees. The career development plans need to be integrated with appropriate training sessions and upskilling processes for the workers to improve their competencies (Ma Janice et al. 2023). Similarly, AHNAIZN Business Group can also offer their employees career development strategies to improve their employee retention rates. Offering the employees with flexible working hours can also help in retaining employees.
Flexible working hours provide the workers with the opportunity to work at their suitable time. As a result, employees can maintain their personal and professional obligations adequately. Flexible working promotes a proper work-life balance for the workers, which can help the organisation in attracting talent (Lee and Kim, 2023). AHNAIZN can integrate flexible working for their employees to increase employee satisfaction, which in turn reduces employee turnover rate. It also exerts a positive impact on employee commitment and motivation. Additionally, HR professionals need to research the market to determine adequate remuneration for their employees (Li et al. 2023). The staff wages need to be aligned with the market standard to maintain adequate employee motivation. Providing proper compensation packages makes employees feel valued at their work and enhances their motivation toward increasing efforts and commitment to the organisation. AHNAIZN can provide the employees with higher wages relying on the market standard to facilitate employee retention.
5.4. Limitation
The study has employed a mixed approach to collect qualitative and quantitative data through survey and secondary data collection. Obtaining primary data from the survey process has helped in gaining quantitative information. However, it has limited the process of evaluating the behaviour and perspective of the participants regarding employee retention processes in a broader manner. Therefore, conducting semi-structured interviews could have provided more information regarding employee retention.
5.5. Future research scope
The future research scope has highlighted a few research questions, which can be further explored for additional research on this topic.
• How do external forces affect the HRM practices of business firms?
• What are the common challenges faced by the HRM department in employee retention?
• How the common challenges in employee retention can be resolved to increase the effectiveness of HRM?
• What is the impact of advanced technology in traditional HRM practices, which has facilitated employee retention techniques?
6. Reflection
I have done an HRM internship at a prominent UK-based company known as AHNAIZN Business Group. I have explored various aspects of HRM and gathered knowledge regarding how HRM play a significant role in shaping organisational dynamics and building a positive workplace environment. I am about to use “Gibbs’ Reflective Cycle” to explore my experience and determine my learning through this internship. The “Gibbs’ Reflective Cycle” has six steps such as “description”, “feelings”, “evaluation”, “analysis”, “conclusion”, and “action plan” (Adeani et al. 2020). This reflective cycle plays a crucial role in evaluating one’s perspective and knowledge gained throughout a project.
Figure 6.1: Gibbs’ Reflective Model
(Source: Adeani et al. 2020)
Description
The exploration of HRM across various grounds during my internship at AHNAIZN allows me a comprehensive view of HRM’s crucial role in the organisation’s ground. My journey went through a deeper exploration of the purpose of HRM, uncovering its fundamental role and contribution, which helps an organisation achieve its goals. During the internship, I realised that the HRM is quite a complex matter within a company. The more I research and understand the functions and responsibilities of HRM the more I am able to know that it goes beyond the usual or typical roles. HRM is more diverse and involves various tasks such as employee recruitment, selection, personal development, developing policies to increase employee retention and more (Zardasht et al. 2020). HRM also plays a significant role in talent acquisition and it can be described as a crucial part of HRM. I understood that through talent acquisition, HRM makes sure various aspects such as finding, hiring, and integrating new talent into the organisation.
Therefore, it helps to contribute to the process that determines how the organisation operates. I think it also highlights the relationship between HRM and talent acquisition strategies, which make sure that the skills and expertise of individuals match the overall goals of the organisation. Furthermore, as I delve deeper into the concept of HRM, it allows me to explore the activities HRM does in conflict resolution. I can say that HRM plays a significant role in conflict handling by establishing itself as a mediator and facilitator, which tackles conflicts that arise between individuals or within the organisation. The importance of addressing conflict is significant, which requires HRM to establish clear policies for resolving conflicts and provide training programs to increase employees’ understanding (Stankevičiūtė and Savanevičienė, 2021). I realised that it not only helps to minimise conflict within an organisation but plays a crucial role in developing a positive work environment.
Feelings
The opportunity of the internship at AHNAIZN has provided a deep appreciation for the many different aspects of HRM. I realise that HRM maintains a delicate balance within a company and it is also complex and has a significant impact on various aspects of organisational life. My emotional response to understanding the function of HRM can be linked with the unfolding of a mystery. Understanding HRM can reveal interconnected elements that contribute to the overall picture of an organisation (Ererdi et al. 2022). The role of HRM in shaping the culture of the workplace can be compared with the unseen force of nature that guides the development of our surrounding environment. I have also explored how HRM affects employee satisfaction by creating a sense of empathy and understanding for them.
Evaluation
Looking back allowed me to realise how well the HRM of AHNAIZN was communicated during their internship. The strategic examples and explanations were crucial for me in gaining a clear understanding of how HRM affects various aspects of an organisation. However, I believe that the experience of my internship journey could be better in case I could communicate more with existing employees of AHNAIZN. The real situations I faced during the internship acted as clear examples of the theoretical concepts related to HRM. In addition, real-world scenarios and discussions have successfully connected theoretical ideas to practical situations. Breaking down complex activities for managing talent to approaches for resolving conflicts allowed me a thorough exploration and understanding of each aspect of HRM.
Analysis
Analysing the discussed ideas and approaches in the reflection reveals that HRM has a strategic and significant effect on the outcomes of an organisation. One of the most important parts of HRM is that it contributes to the strategic connection between the functions of HRM and the overall goals of the organisation (Azevedo et al. 2021). For example, analysing talent acquisition strategies shows that it is not only about hiring people but involves a strategic process of identifying skills that can be aligned with the goals of the company by bringing them on board. Analysing conflict management activities shows that HRM works as a mediator in the process of handling conflicts within the organisation. Furthermore, the feedback process within the HRM can be referred to as a strategy, which allows creating an ongoing conversation between workers and higher officials.
Conclusion
Reaching the conclusion based on the exploration of “Gibbs’s reflection model” brings together the various aspects of HRM that I encountered during my internship at AHNAIZN. It allowed me to understand the essential role of HRM in today’s corporate world. The success and rapid growth of businesses such as AHNAIZN significantly depends on the effective implementation of HRM practices (Mayrhofer et al. 2021). The conclusion of the importance of talent acquisition is crucial in the context of HRM practice. The process of identifying, recruiting, and onboarding talent plays a significant role in the positive growth of a firm (Zhou et al. 2021). Similarly, the importance of conflict resolution is also vital for maintaining the overall well-being and unity of the organisation.
Action plan
The problem I faced due to the lack of opportunities to communicate with existing employees required to be solved in future. Addressing this issue would require me to focus on project time management. Project time management allows one to divide and prioritise tasks, which helps to perform tasks with efficiency without wasting time on less important factors (Adams and Blair, 2019). Therefore, it is expected to enhance my overall project time management quality. Furthermore, the action plan outlines a commitment, which can provide opportunities for me to work on personal development.
References
Ababneh, O.M.A., 2021. How do green HRM practices affect employees’ green behaviors? The role of employee engagement and personality attributes. Journal of Environmental Planning and Management, 64(7), pp.1204-1226.
Acampora, A., Lucchetti, M.C., Merli, R. and Ali, F., 2022. The theoretical development and research methodology in green hotels research: A systematic literature review. Journal of Hospitality and Tourism Management, 51, pp.512-528.
Adams, R.V. and Blair, E., 2019. Impact of time management behaviors on undergraduate engineering students’ performance. Sage Open, 9(1), p.2158244018824506.
Adeani, I.S., Febriani, R.B. and Syafryadin, S., 2020. Using GIBBS’reflective cycle in making reflections of literary analysis. Indonesian EFL Journal, 6(2), pp.139-148.
AHNAIZN, 2023. AHNAIZN – Business Group. [Online]. Available at: https://ahnaizn.com/ [Accessed on 19-10-2023]
Al-Ababneh, M.M., 2020. Linking ontology, epistemology and research methodology. Science & Philosophy, 8(1), pp.75-91.
Al-Swidi, A.K., Gelaidan, H.M. and Saleh, R.M., 2021. The joint impact of green human resource management, leadership and organizational culture on employees’ green behaviour and organisational environmental performance. Journal of Cleaner Production, 316, p.128112.
Anbu, D., 2019. A review on human resources management (HRM) theories and effective human resource management models. Asian Journal of Multidimensional Research (AJMR), 8(5), pp.81-93.
Azevedo, M.C.D., Schlosser, F. and McPhee, D., 2021. Building organizational innovation through HRM, employee voice and engagement. Personnel Review, 50(2), pp.751-769.
Babii, A., 2020. Important aspects of the experimental research methodology. Вісник Тернопільського національного технічного університету, 97(1), pp.77-87.
Botelho, C., 2020. The influence of organizational culture and HRM on building innovative capability. International Journal of Productivity and Performance Management, 69(7), pp.1373-1393.
Budianto, A., 2020. Legal research methodology reposition in research on social science. International Journal of Criminology and Sociology, 9(1), pp.1339-1346.
Burnett, J.R. and Lisk, T.C., 2021. The future of employee engagement: Real-time monitoring and digital tools for engaging a workforce. In International Perspectives on Employee Engagement (pp. 117-128). Routledge.
Chams, N. and García-Blandón, J., 2019. On the importance of sustainable human resource management for the adoption of sustainable development goals. Resources, Conservation and Recycling, 141, pp.109-122.
Chivanga, S.Y. and Monyai, P.B., 2021. Back to basics: Qualitative research methodology for beginners. Journal of Critical Reviews, 8(2), pp.11-17.
Chong, L., Ngolob, R.A. and Palaoang, T.D., 2020. Human resource management (HRM) practices. Journal of Advanced Management Science, 8(4).
Dalessandro, C. and Lovell, A. 2023, “Influence and Inequality: Worker Identities and Assessments of Influence over Workplace Decisions”, Social Sciences, vol. 12, no. 4, pp. 205.
Davidescu, A.A., Apostu, S.A., Paul, A. and Casuneanu, I., 2020. Work flexibility, job satisfaction, and job performance among Romanian employees—Implications for sustainable human resource management. Sustainability, 12(15), p.6086.
Delios, A., Welch, C., Nielsen, B., Aguinis, H. and Brewster, C., 2023. Reconsidering, refashioning, and reconceptualizing research methodology in international business. Journal of World Business, 58(6), p.101488.
Djafar, H., Yunus, R., Pomalato, S.W.D. and Rasid, R., 2021. Qualitative and Quantitative Paradigm Constellation In Educational Research Methodology. International Journal of Educational Research and Social Sciences (IJERSC), 2(2), pp.339-345.
Dodds, S. and Hess, A.C., 2020. Adapting research methodology during COVID-19: lessons for transformative service research. Journal of Service Management, 32(2), pp.203-217.
Dzwigol, H., 2022. Research methodology in management science: Triangulation. Virtual Economics, 5(1), pp.78-93.
El-Sharkawy, S., Nafea, M.S. and Hassan, E.E.H. 2023, “HRM and organizational learning in knowledge economy: investigating the impact of happiness at work (HAW) on organizational learning capability (OLC)”, Future Business Journal, vol. 9, no. 1, pp. 10.
Ererdi, C., Nurgabdeshov, A., Kozhakhmet, S., Rofcanin, Y. and Demirbag, M., 2022. International HRM in the context of uncertainty and crisis: A systematic review of literature (2000–2018). The International Journal of Human Resource Management, 33(12), pp.2503-2540.
Eva, N., Meacham, H., Newman, A., Schwarz, G. and Tham, T.L., 2019. Is coworker feedback more important than supervisor feedback for increasing innovative behavior?. Human Resource Management, 58(4), pp.383-396.
Franzoni, S., Sarwar, H. and Ishaq, M.I., 2021. The Mediating Role of HRM in the Relationship between CSR and Performance in the Hospitality Industry. Sustainability, 13(24), p.13699.
Gelencsér, M., Szabó-Szentgróti, G., Zsolt Sándor Kőmüves and Hollósy-Vadász, G. 2023, “The Holistic Model of Labour Retention: The Impact of Workplace Wellbeing Factors on Employee Retention”, Administrative Sciences, vol. 13, no. 5, pp. 121.
Ghani, B., Zada, M., Khalid, R.M., Ullah, R., Khattak, A., Han, H., Ariza-Montes, A. and Araya-Castillo, L. 2022, “Challenges and Strategies for Employee Retention in the Hospitality Industry: A Review”, Sustainability, vol. 14, no. 5, pp. 2885.
Greening, N., 2019. Phenomenological research methodology. Scientific Research Journal, 7(5), pp.88-92.
Hassan, M., Jambulingam, M., Alam, M.N. and Islam, S., 2019. Redesigning the retention strategy against the emerging turnover of Generation Y: Revisiting the long-standing problems from 20Th to 21St century. International Journal of Entrepreneurship, 23(2), pp.1-16.
Hassan, Z., 2022. Employee retention through effective human resource management practices in Maldives: Mediation effects of compensation and rewards system. Journal of Entrepreneurship, Management and Innovation, 18(2), pp.137-174.
Hassan, Z., 2022. Employee retention through effective human resource management practices in Maldives: Mediation effects of compensation and rewards system. Journal of Entrepreneurship, Management and Innovation, 18(2), pp.137-174.
Inoyatova, S., 2021. HRM & job satisfaction: case of Uzbekistan. Sosyal Araştırmalar ve Davranış Bilimleri, 7(14), pp.165-180.
Iovino, F. and Tsitsianis, N., 2020. The methodology of the research. In Changes in European energy markets (pp. 79-95). Emerald Publishing Limited.
Islam, M.A., Hack‐Polay, D., Haque, A., Rahman, M. and Hossain, M.S., 2022. Moderating role of psychological empowerment on the relationship between green HRM practices and millennial employee retention in the hotel industry of Bangladesh. Business Strategy & Development, 5(1), pp.17-29.
Islam, M.A., Mendy, J., Haque, A.A. and Rahman, M., 2022. Green human resource management practices and millennial employees’ retention in small and medium enterprises: The moderating impact of creativity climate from a developing country perspective. Business Strategy & Development, 5(4), pp.335-349.
Jacob, M.E., 2021. A study on factors affecting employee retention through HRM practices in SME. Journal of Management Research, 11(4), pp.37-53.
Jam, M. and Jamal, W.N., 2020. Impact of green human resources management practices on organizational sustainability and employee retention: An empirical study related to educational institutions. iRASD Journal of Management, 2(1), pp.38-48.
John-Eke, E.C. and Akintokunbo, O.O., 2020. Conflict management as a tool for increasing organizational effectiveness: A review of literature. International Journal of Academic Research in Business and Social Sciences, 10(5), pp.299-311.
Kong, Y., Antwi‐Adjei, A. and Bawuah, J., 2020. A systematic review of the business case for corporate social responsibility and firm performance. Corporate Social Responsibility and Environmental Management, 27(2), pp.444-454.
Kravariti, F. and Johnston, K., 2020. Talent management: a critical literature review and research agenda for public sector human resource management. Public Management Review, 22(1), pp.75-95.
Lee, E.S. and Szkudlarek, B., 2021. Refugee employment support: The HRM–CSR nexus and stakeholder co‐dependency. Human Resource Management Journal, 31(4), pp.936-955.
Lee, E.S. and Szkudlarek, B., 2021. Refugee employment support: The HRM–CSR nexus and stakeholder co‐dependency. Human Resource Management Journal, 31(4), pp.936-955.
Lee, M. and Kim, B. 2023, “Effect of Employee Experience on Organizational Commitment: Case of South Korea”, Behavioral Sciences, vol. 13, no. 7, pp. 521.
Li, M., Malik, M.S., Ijaz, M. and Irfan, M. 2023, “Employer Responses to Poaching on Employee Productivity: The Mediating Role of Organizational Agility in Technology Companies”, Sustainability, vol. 15, no. 6, pp. 5369.
Ma Janice, J.G., Emil Renfred, A.R. and German, J.D. 2023, “Sustainable Ergonomic Workplace: Fostering Job Satisfaction and Productivity among Business Process Outsourcing (BPO) Workers”, Sustainability, vol. 15, no. 18, pp. 13516.
Mahdy, F., Alqahtani, M. and Binzafrah, F. 2023, “Imperatives, Benefits, and Initiatives of Green Human Resource Management (GHRM): A Systematic Literature Review”, Sustainability, vol. 15, no. 6, pp. 4866.
Malik, E., Baig, S.A. and Manzoor, U., 2020. Effect of HR practices on employee retention: The role of perceived supervisor support. Journal of Public Value and Administrative Insight, 3(1), pp.1-7.
Mardiana, S., 2020. Modifying Research Onion for Information Systems Research. Solid State Technology, 63(4), pp.5304-5313.
Mayrhofer, W., Gooderham, P.N. and Brewster, C., 2021. Context and HRM: theory, evidence, and proposals. In Comparative Human Resource Management (pp. 15-31). Routledge.
Meier, O., Naccache, P. and Schier, G., 2021. Exploring the curvature of the relationship between HRM–CSR and corporate financial performance. Journal of Business Ethics, 170, pp.857-873.
Mira, M., Choong, Y. and Thim, C., 2019. The effect of HRM practices and employees’ job satisfaction on employee performance. Management Science Letters, 9(6), pp.771-786.
Mohamed Husni, A.A. and Jais, J. 2023, “Analyzing the influence of decision making and effective employee communication on human resource agility in commercial banks: A mediation role for job satisfaction”, Cogent Social Sciences, vol. 9, no. 1.
Nash, D. and Hann, D., 2020. Strategic conflict management? A study of workplace dispute resolution in Wales. ILR Review, 73(2), pp.411-430.
Newman, M. and Gough, D., 2020. Systematic reviews in educational research: Methodology, perspectives and application. Systematic reviews in educational research: Methodology, perspectives and application, pp.3-22.
Okbagaber, T.B., 2019. The effect of human resources management on employees retention in IBM Corporation. Journal of Asian Business Strategy, 9(2), p.158.
Okojie, G., Ismail, I.R., Begum, H., A S A Ferdous, A. and Elkhan Richard Sadik-Zada 2023, “The Mediating Role of Social Support on the Relationship between Employee Resilience and Employee Engagement”, Sustainability, vol. 15, no. 10, pp. 7950.
Öztürk, O. and Esra, D.İ.L., 2022. Bibliometric Analysis of Organizational Ecology Theory (OET): To Review Past for Directing the Future of the Field. Ege Academic Review, 22(2), pp.195-212.
Papa, A., Dezi, L., Gregori, G.L., Mueller, J. and Miglietta, N., 2020. Improving innovation performance through knowledge acquisition: the moderating role of employee retention and human resource management practices. Journal of Knowledge Management, 24(3), pp.589-605.
Papa, A., Dezi, L., Gregori, G.L., Mueller, J. and Miglietta, N., 2020. Improving innovation performance through knowledge acquisition: the moderating role of employee retention and human resource management practices. Journal of Knowledge Management, 24(3), pp.589-605.
Patel, M. and Patel, N., 2019. Exploring research methodology. International Journal of Research and Review, 6(3), pp.48-55.
Piwowar‐Sulej, K., 2021. Core functions of Sustainable Human Resource Management. A hybrid literature review with the use of H‐Classics methodology. Sustainable Development, 29(4), pp.671-693.
Podgorodnichenko, N., Edgar, F. and McAndrew, I., 2020. The role of HRM in developing sustainable organizations: Contemporary challenges and contradictions. Human Resource Management Review, 30(3), p.100685.
Podgorodnichenko, N., Edgar, F. and McAndrew, I., 2020. The role of HRM in developing sustainable organizations: Contemporary challenges and contradictions. Human Resource Management Review, 30(3), p.100685.
Rahim, M.A. and Katz, J.P., 2020. Forty years of conflict: the effects of gender and generation on conflict-management strategies. International Journal of Conflict Management, 31(1), pp.1-16.
Rajput, N., Das, G., Shivam, K., Nayak, C.K., Gaurav, K. and Nagpal, P., 2023. An inclusive systematic investigation of human resource management practice in harnessing human capital. Materials Today: Proceedings, 80, pp.3686-3690.
Ramapriya, M. and Sudhamathi, S., 2020. Theory of employee retention strategies. Journal of Interdisciplinary Cycle Research, 7(2), pp.1111-1119.
References
Roscoe, S., Subramanian, N., Jabbour, C.J. and Chong, T., 2019. Green human resource management and the enablers of green organisational culture: Enhancing a firm’s environmental performance for sustainable development. Business Strategy and the Environment, 28(5), pp.737-749.
Rumsey, M., Stowers, P., Sam, H., Neill, A., Rodrigues, N., Brooks, F. and Daly, J., 2022. Development of PARcific approach: participatory action research methodology for collectivist health research. Qualitative Health Research, 32(8-9), pp.1297-1314.
Ryder, C., Mackean, T., Coombs, J., Williams, H., Hunter, K., Holland, A.J. and Ivers, R.Q., 2020. Indigenous research methodology–weaving a research interface. International Journal of Social Research Methodology, 23(3), pp.255-267.
Santana, M., Morales-Sánchez, R. and Pasamar, S., 2020. Mapping the link between corporate social responsibility (CSR) and human resource management (HRM): how is this relationship measured?. Sustainability, 12(4), p.1678.
Sarvaiya, H., Arrowsmith, J. and Eweje, G., 2021. Exploring HRM involvement in CSR: variation of Ulrich’s HR roles by organisational context. The International Journal of Human Resource Management, 32(21), pp.4429-4462.
Sawaneh, I.A. and Kamara, F.K., 2019. An effective employee retention policies as a way to boost organizational performance. Journal of Human Resource Management, 7(2), pp.41-48.
Sepahvand, R. and Bagherzadeh Khodashahri, R., 2021. Strategic human resource management practices and employee retention: A study of the moderating role of job engagement. Iranian Journal of Management Studies, 14(2), pp.437-468.
Shin, D., Garmendia, A., Ali, M., Konrad, A.M. and Madinabeitia-Olabarria, D., 2020. HRM systems and employee affective commitment: The role of employee gender. Gender in Management: An International Journal, 35(2), pp.189-210.
Sileyew, K.J., 2019. Research design and methodology. Cyberspace, pp.1-12.
Škerháková, V., Korba, P., Harničárová, M. and Taha, V.A. 2022, “Talent Retention: Analysis of the Antecedents of Talented Employees’ Intention to Stay in the Organizations”, European Journal of Interdisciplinary Studies, vol. 14, no. 1, pp. 56-67.
Snyder, H., 2019. Literature review as a research methodology: An overview and guidelines. Journal of business research, 104, pp.333-339.
Sobhani, F.A., Haque, A. and Rahman, S., 2021. Socially responsible HRM, employee attitude, and bank reputation: the rise of CSR in Bangladesh. Sustainability, 13(5), p.2753.
Stahl, G.K., Brewster, C.J., Collings, D.G. and Hajro, A., 2020. Enhancing the role of human resource management in corporate sustainability and social responsibility: A multi-stakeholder, multidimensional approach to HRM. Human Resource Management Review, 30(3), p.100708.
Stankevičiūtė, Ž. and Savanevičienė, A., 2021. Can sustainable HRM reduce work-related stress, work-family conflict, and burnout?. In International Perspectives on Employee Engagement (pp. 88-107). Routledge.
Statista, 2023. Human resources applications implemented in the last 12 months worldwide in 2019, by type. [Online]. Available at: https://www.statista.com/statistics/1085944/human-resources-applications-implemented-worldwide/ [Accessed on 31-10-2023]
Statista, 2023. Human resources professionals strategies to accelerate employees’ skill development worldwide 2021. [Online]. Available at: https://www.statista.com/statistics/1235402/hr-professionals-plans-to-accelerate-skill-development/ [Accessed on 31-10-2023]
Statista, 2023. Main factors contributing to recruiting and retention challenges in the United States as of 2023. [Online]. Available at: https://www.statista.com/statistics/1332197/factors-influencing-recruitment-retention-problems-worldwide/ [Accessed on 31-10-2023]
Statista, 2023. Why People Are Quitting Their Jobs. [Online]. Available at: https://www.statista.com/chart/27830/reasons-for-quitting-previous-job/ [Accessed on 19-10-2023]
Suharti, L. and Sugiarto, A., 2020. A qualitative study OF Green HRM practices and their benefits in the organization: An Indonesian company experience. Business: Theory and Practice, 21(1), pp.200-211.
Tayebi Abolhasani, A., 2019. Introduction to research methodology: Standard procedures for qualitative data analysis. Science and Technology Policy Letters, 9(2), pp.67-96.
Tej, J., Vagaš, M., Viktória, A.T., Škerháková, V. and Harničárová, M. 2021, “Examining HRM Practices in Relation to the Retention and Commitment of Talented Employees”, Sustainability, vol. 13, no. 24, pp. 13923.
Townley, B., 2019. Foucault, power/knowledge, and its relevance for human resource management. In Postmodern management theory (pp. 215-242). Routledge.
Urcia, I.A., 2021. Comparisons of adaptations in grounded theory and phenomenology: Selecting the specific qualitative research methodology. International journal of qualitative methods, 20, p.16094069211045474.
Vargas-Hernández, J.G., Rakowska, J. and Vargas-González, M.O.C., 2022. Interface of Organisational Ageing and Organisational Ecology Theory. Marketing of Scientific and Research Organizations, 45(3), pp.57-70.
Vebrianto, R., Thahir, M., Putriani, Z., Mahartika, I. and Ilhami, A., 2020. Mixed Methods Research: Trends and Issues in Research Methodology. Bedelau: Journal of Education and Learning, 1(2), pp.63-73.
Willmott, H., 2020. On research methodology. The Journal of Organization and Discourse, 1(1), pp.1-4.
Wilton, N., 2019. An introduction to human resource management. An Introduction to Human Resource Management, pp.1-632.
Xiang, H., Lu, J., Kosov, M.E., Volkova, M.V., Ponkratov, V.V., Masterov, A.I., Elyakova, I.D., Popkov, S.Y., Taburov, D.Y., Lazareva, N.V., Muda, I., Vasiljeva, M.V. and Zekiy, A.O. 2023, “Sustainable Development of Employee Lifecycle Management in the Age of Global Challenges: Evidence from China, Russia, and Indonesia”, Sustainability, vol. 15, no. 6, pp. 4987.
Yong, J.Y., Yusliza, M.Y., Ramayah, T., Chiappetta Jabbour, C.J., Sehnem, S. and Mani, V., 2020. Pathways towards sustainability in manufacturing organizations: Empirical evidence on the role of green human resource management. Business Strategy and the Environment, 29(1), pp.212-228.
Zardasht, P., Omed, S. and Taha, S., 2020. Importance of HRM policies on employee job satisfaction. Black Sea Journal of Management and Marketing, 1(1), pp.49-57.
Zhou, Y., Liu, G., Chang, X. and Wang, L., 2021. The impact of HRM digitalization on firm performance: investigating three‐way interactions. Asia Pacific Journal of Human Resources, 59(1), pp.20-43.
