ADDRESSING KEY CHALLENGES AT MORGAN SINDALL: A RESEARCH-DRIVEN ANALYSIS
Executive summery
The study’s goal is to explore the difficulties Morgan Sindall has faced with crisis management, performance management, and economic shock—specifically, during the COVID-19 epidemic and the effects of Brexit. By investigating the instance of Morgan Sindall, the study is extremely important for understanding the significance of performance management and crisis management in the construction business.
The first section highlights the challenges of performance management of Morgan Sindall. The UK’s construction industry has noticed a shortage of labour because of restrictions on hiring immigrants. It has resulted in a severe lack of skilled labour, which has had an impact on Morgan Sindall’s performance. Due to inefficiencies in delivery and other factors, the organization’s property service division has had an operational loss of GBP 4.1 million. Due to social conventions of social distance and disturbances in the supply chain, the COVID-19 epidemic has significantly increased the level of unemployment in the construction industry.
The second section deals with the capability of handling the economic shock of Morgan Sindall. Due to the complexity of regulations and increased cost of importation, one of the frequent issues the company has encountered is importing raw materials for its building projects. For Morgan Sindall, the effects of Brexit on the availability of construction materials were quite evident. The uncertainty brought on by Brexit hampered the company’s ability to purchase components from other parts of the world, including the EU. The rise in import fees and tariffs was one of the biggest problems.
The third section examines the crisis management planning of the organisation to evaluate its challenges. “Mitroff’s Five-Stage Crisis Management Model” has been used by Morgan Sindall to adhere to a certain procedure while dealing with its difficulties. Due to limitations in corporate operations, Morgan Sindall has encountered a major obstacle during the COVID-19 epidemic. The firm noticed a 60% drop in pre-tax earnings in 2020, which is equivalent to about GBP 40 million. Following Brexit, the cost of labour and materials for the building has increased considerably, having an impact on how a UK construction company operates.
Introduction
“Human Resource Management or HRM” is an integral part of the business industry, which is generally associated with recruitment, training, onboarding, and policymaking. In recent years, HRM has played a vital role in incorporating effective policies to obtain higher employee performance through controlling employee turnover and managing employee motivation in their job roles. It has emerged as one of the most important parts of multinational business firms in managing their large and diverse workforce. Morgan Sindall is a leading construction and regeneration enterprise, headquartered in London. The firm has an annual revenue of GBP 3.6 billion and currently employs 7,600 operating across regulated private and public sectors. The organisation has faced significant challenges during the COVID-19 pandemic and has struggled to incorporate the changes in the aftermath of Brexit.
This report analyses the challenges of Morgan Sindall concerning performance management, economic shock, and crisis management to evaluate its challenges and provide effective recommendations. The study has been segmented into three sections to dedicate an in-depth assessment of the challenges faced by Morgan Sindall in the UK. The purpose of the study is to examine the challenges of Morgan Sindall regarding crisis management, performance management, and economic shock, which have been specifically observed during the impact of Brexit and the COVID-19 pandemic. The study is highly significant in comprehending the importance of performance management and crisis management in the construction industry by examining the case of Morgan Sindall. It also assesses the challenges of the firm regarding economic shock and highlights recommendations, which can be essential to understanding the impact of external factors on overall productivity.
Body
Section 1
Performance management is a process of continuous interaction between the employees and the managers to ensure continuous feedback and communication, which helps the organisation achieve strategic goals (Pugna et al. 2019). Morgan Sindall is using “KPIs or Key Performance Indicators” to measure the firm’s performance and challenging targets (Morgan Sindall, 2023). The organisation uses a wide variety of KPIs to measure its productivity; such as “Lost time incident rate (LTIR)”, “number of training days per employee per year”, “reduction in carbon emission”, and “Average monetary value of social activities”. Additionally, the firm strives toward excelling in project delivery to the end-users and customers along with maintaining quality by selecting appropriate projects. Additionally, MS aims to secure long-term workstreams by establishing positive partnerships with workers, clients, and suppliers. Moreover, the organisation has been committed to protecting people and the environment through innovating and improving its supply chain.
However, the organisation has been facing significant challenges due to labour shortage in the UK due to Brexit. Due to the restrictions related to immigrant workers, the construction industry of the UK has observed a shortfall of construction workers. It has led to a significant shortage of skilled workers, which has affected the performance of Morgan Sindall. The property service business of the organisation has generated a GBP 4.1 million operating loss due to delivery issues and inefficiencies. The COVID-19 pandemic has led to a significant rise in the unemployment rate in the construction sector due to social distancing norms and supply chain disruptions (Elmarzouky et al. 2021). The UK economy began to revive as the government relaxed the COVID-19 restrictions and construction projects resumed. However, it has revealed a huge shortage of skilled employees as the majority of the migrant workers left the UK due to Brexit.
As an EU member, the UK construction sector relied on the free movement of workers from other European countries. Around 40% of construction workers in the United Kingdom were from Europe. On the other hand, the “Construction Industry Training Board (CITB)” has predicted that over the next ten years, over 1 million construction employees will be reaching retirement age through their “Construction Skills Network” initiative. It has highlighted an upcoming skill gap in the construction industry, which has facilitated additional efforts from the UK government to expand its workforce especially related to the construction industry. Hence, the British government has focused on expanding the number of individuals entering the construction industry (Hutahayan, 2020). However, it will not be sufficient to meet the needs of construction workers in the coming years. The negative impact of Brexit has been emphasised by a rise in expensive and complicated construction projects in the United Kingdom.
Due to the introduction of a “points-based immigration system” by the UK government, migrant workers will be unable to obtain visas leading to a significant skill gap in the industry. The “EU-UK Trade and Cooperation Agreement (TCA)” established this system, which requires employees to have at least 70 points to obtain visas to work in the UK. Morgan Sindall has faced additional costs for the initiation phases of the mobilised contracts. The organisation has been trying to improve its senior management team to enhance its client services and adequate operation delivery (Shet et al. 2019). Moreover, the organisation has observed a decline in operating profit to 27%, which amounts approximately to GBP 10.1 million due to the increasing rate of mortgages and economic uncertainty in the UK. The firm has also noticed a decrease in net cash around GBP 11 million-263 million, which has facilitated the firm in revising its operational expenses to GBP 400,000 to GBP 48.5 million (Building.co.uk, 2023).
Morgan Sindall can focus on hiring native employees to reduce the negative impact of the employee shortage. The organisation can offer the employees higher remunerations and additional benefits to attract skilled workers to reduce its operational inefficiencies to decrease the chances of project delivery issues (Richards et al. 2019). As the UK is facing a significant challenge in the shortage of skilled labour, the organisation can start integrated training programmes for the existing employees to upskill and reskill. It will help the firm in providing the workers with a significant career development plan and it will assist the organisation in training its existing workforce following the industry standard (McDermott et al. 2019). Moreover, Morgan Sindall can also develop training programmes for aspirants, who are interested in the construction industry. It can help the firm in attracting top talents from the university campus to further strengthen its workforce.
In this way, the enterprise can train its workforce according to its core values and required expertise, which can help the firm resolve its challenges of operational inefficiencies. In this context, the firm will also be able to help the local communities and contribute to local people through providing employment opportunities.
Section 2
An economic shock is a sudden and unexpected event that can shake up the economy. It takes place when something unexpected happens that interrupts the business transaction and it can greatly influence how an organisation’s economy works. An economic shock can affect Morgan Sindall by influencing its construction projects and financial stability. For instance, a recession may lead to reduced construction demand, while higher material costs due to inflation can increase project expenses, affecting the company’s profitability and growth prospects (Bissoondeeal et al. 2023). One of the common problems the firm has faced is importing the raw materials for its construction projects due to the complexity of regulation and increased cost of importing. Morgan Sindall has a strategic approach where they purchase their raw materials in advance to avoid any uncertainty in business transactions.
However, after the UK left the EU, which is also known as Brexit has uncertainties and challenges related to the availability of construction materials for companies such as Morgan Sindall. The firm depends on a complex supply chain for raw materials supplies from various regions, which has created uncertainty in stocking supplies due to Brexit (Gupta et al. 2023). The raw materials that are barely available locally are required to be imported from other regions, which increases the cost of import due to the absence of benefits that UK companies used to get through the UK’s collaboration with the EU. The impact of Brexit on the availability of construction materials had clear consequences for Morgan Sindall. As the company relied on a complex supply chain to source materials from various regions, including the EU, the uncertainties brought by Brexit disrupted this essential flow (Walsh et al. 2022).
One significant challenge stemmed from the increase in importing costs and tariffs. These unexpected expenses, which were not originally counted into project budgets, put pressure on the firm’s profitability (Rakha et al. 2021). Although the company had proactively stockpiled certain construction materials before Brexit, the passage of time revealed new problems. Shortages in raw materials began to emerge, leading to project delays and intensifying competition for the limited available resources (McCann et al. 2023). This heightened competition had the potential to further inflate material prices, compounding the challenges faced by Morgan Sindall in maintaining project timelines and budgets. This economic impact has affected Morgan Sindall including the entire UK construction industry, as the overall UK construction industry revenue was drastically low in the financial year 2020 near about 272.59 GPB.
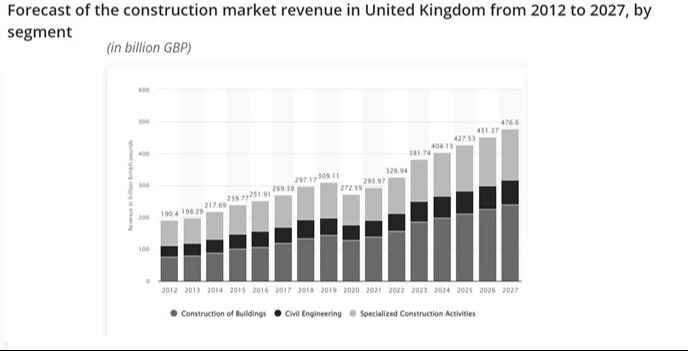
Figure 1: Revenue of the UK construction industry
(Source: Statista, 2023)
The economic performance of Morgan Sindall carries a significant brunt of the COVID-19 pandemic. Due to the pandemic In the first half of 2020 until June, the company faced its most challenging financial outcomes in the past five years. Pre-tax profits dropped sharply by 62%, dwindling to approximately 13.6 million GBP, while turnover witnessed a 4% decline, resting at 1.4 billion GBP (Malik et al. 2019). The repercussions of COVID-19 were clear in the company’s quarterly performance. The initial quarter displayed promise with a 17% increase in revenue compared to the preceding year. However, the second quarter carried the full impact of the pandemic, as income nosedived by 23%. April, the first complete month of the lockdown, stands out for its remarkable and critical 35% drop in turnover.
The company’s biggest division, which deals with construction and infrastructure, saw a significant increase in revenue, up by 16% to 789 million GBP. However, a substantial 17% drop in operating profit, which amounted to 11.5 million GBP, accompanied this growth. The impact of COVID-19 was strongly observed at Morgan Sindall’s construction sites and infrastructure projects (McCann et al. 2023). The company had to use its contractual rights to address delays and closures, affecting about 45% of its commitments. In summary, the pandemic had a big impact on Morgan Sindall’s finances, causing lower profits, disruptions in different parts of its business, project delays, temporary shutdowns, and unexpected extra expenses. This shows how far-reaching the pandemic’s effects were, not only on the company but also on the construction industry and the overall economy.
Morgan Sindall can increase its ability to tackle economic shocks and supply chain disruptions by diversifying its suppliers of raw materials to reduce reliance on specific suppliers or regions. The organisation also need to utilise a proactive stockpiling approach along with evaluating and updating its stockpile regularly. Importing expenses can be reduced by assessing for post-Brexit legislative changes and examining cost-benefit evaluations for local sourcing (Ataei and Taherkhani, 2019). Enhancing contractual safeguards and establishing a solid risk management strategy is also essential for effectively handling unanticipated supply chain disruptions similar to the pandemic period. Working together with similar companies and associations related to the construction industry can offer insightful guidance for overcoming obstacles in the construction sector for Morgan Sindall. These strategies can give Morgan Sindall the ability to strengthen its financial position in the construction market of the UK and guarantee the successful and timely completion of building projects despite economic uncertainty.
Section 3
Crisis management planning is the process of the business organisation preparing for adverse situations. It informs the way of responding to a crisis to minimise damage and restore positive business operational activities. Morgan Sindall has been using “Mitroff’s Five-Stage Crisis Management Model” to follow a definite process to address its challenges (Bhaduri, 2019). At the first stage of the model “signal detection”, the warning signs are generally detected and given significant effort to prevent the negative impact. In the second stage, the organisation search for risk factors and the probability of damage in the operational process. The “damage containment” stage highlights the importance of keeping the problems contained to reduce spreading and implement effective strategies to eradicate the issues (Berbekova et al. 2021). The recovery stage depicts the age after the resolution of the challenges and “learning” informs analysing the event to gain insight into the situation. This model has assisted Morgan Sindall in withstanding various industry challenges.
During the COVID-19 pandemic, Morgan Sindall has faced a significant challenge due to restrictions in business operations. Due to the governmental restriction, the majority of the construction firms including Morgan Sindall stopped their operational process to maintain social distancing and other safety measures during the pandemic. It has led to a huge decrease in profit, which has appeared to be the lowest profit in the last five years (Hassankhani et al. 2021). In 2020, the organisation observed a decrease in pre-tax profit, which is around 60%, which amounts to approximately GBP 40 million. The organisation has increased its liquidity in this period with GBP 153 million/day cash compared to GBP 123 million/day from the pre-pandemic period (Constructionnews.co.uk, 2023). It has helped the organisation in availing financial resources in critical situations. Despite the effort to withstand the adverse effects of the pandemic, Morgan Sindall suffered a significant loss during the pandemic.
Additionally, the organisation had observed positive COVID cases in their office premises, which facilitated an enquiry from the “Site Project Manager”. The prompt response from the organisation has ensured swift action and priority over the employee’s health and safety. Morgan Sindall was able to start the decontamination process the same day in all affected areas, ensuring the protection of all the personnel and staff members. It highlights that the organisation has been able to provide effective staff security during the pandemic period. On the other hand, Brexit has created an uncertain economic effect for the organisation due to rising costs and inflation (Oyegoke et al. 2023). Following Brexit, the cost of construction materials and personnel has increased dramatically affecting the operational process of the construction firm in the UK. Between 2015 and 2022, the cost of construction materials grew by nearly 60%, which has in turn facilitated the expanses of the building projects (The Guardian, 2023).
It covers the cost of cement, steel, and wood, all of which have increased the overall cost of construction projects, due to shortage of supply and the post-pandemic effect. Along with that, the necessity for construction employees has increased by 30% in the UK, which has also affected the operational process of Morgan Sindall. Brexit has facilitated a 330,000-person deficit in the construction industry, particularly in the “low-skilled sector”, which has resulted in inefficiencies in the delivery process (Gupta et al. 2023). Construction enterprises that make the majority of their income by shipping materials to European countries were severely impacted. Morgan Sindall has been able to minimise the impact of supply chain disruptions due to Brexit and COVID-19, however, supply chain difficulties have remained a huge problem. The firm has concentrated on focused sourcing by managing the supply chain and concentrating on ongoing operational efficiencies (Constructionnews.co.uk, 2023).
Construction enterprises are suffering from the higher expense of resource exporting, resulting in a 35-40% decline in exports. However, the combined effect of Brexit and COVID-19 has affected material and transportation costs along with an increase in fuel prices due to the “Ukraine-Russia conflict”. As a result, construction businesses are devoting more efforts to acquiring raw materials for building projects to reduce operational costs and avoid delayed delivery (Rakha et al. 2021). The higher work force requirement has resulted in increased labour costs and salary increases, which enhances the cost of the infrastructure projects. Furthermore, one of the key concerns about Brexit is the restriction of the free movement of workers and goods, which has created a significant challenge for Morgan Sindall.
Morgan Sindall needs to focus on the local supply chain network to reduce the cost of the projects by reducing transportation costs. Utilising a local supply network can help the firm reduce disruptions due to supply chain challenges. Additionally, the organisation can use data analytics to enhance its crisis management procedures to evaluate information on the global market and consumer requirements (Stride et al. 2023). It can help the firm predict market trends and demand through leveraging predictive analytics. Big data analytics are significantly helpful in analysing past and present market trends to deliver probable future requirements (Pugna et al. 2019). Additionally, it can increase the transparency of the supply chain, through which Morgan Sindall can effectively enhance the performance of its crisis management model and improve its supply chain productivity.
Conclusion
The study has shed light on the various challenges of Morgan Sindall especially highlighting issues of performance management, crisis management, and handling economic shock. Morgan Sindall employs “KPIs or Key Performance Indicators”, to assess the firm’s performance and set demanding goals. The firm measures its productivity using a wide range of KPIs, including “Lost time incident rate (LTIR),” “number of training days per employee per year,” “reduction in carbon emission,” and “Average monetary value of social activities.” However, the firm has faced substantial hurdles because of a worker shortage in the UK because of Brexit. The UK construction industry has seen a shortage of construction employees because of immigration worker restrictions. Morgan Sindall has used “Mitroff’s Five-Stage Crisis Management Model” to manage its difficulties systematically. Morgan Sindall experienced major challenges during the COVID-19 epidemic due to constraints in company activities. Due to legislative restrictions, the bulk of construction enterprises, including Morgan Sindall, ceased operations during the epidemic to preserve social distance and other safety measures. Following Brexit, the cost of construction supplies and employees has skyrocketed, negatively affecting the operational process of the UK construction industry. Morgan Sindall needs to concentrate on the regional vendor network to lower project expenses by reducing transportation expenditures. Using a local supplier network might assist the company in reducing supply chain disruptions. Furthermore, the company can employ data analytics to improve its crisis management methods by evaluating global market and customer needs.
References
Ataei, H.O.S.S.E.I.N. and Taherkhani, F.A.R.N.A.Z., 2019. The brexit and its economic impacts on the construction industry. Proceedings of International Structural Engineering and Construction, 6, pp.10-14455.
Berbekova, A., Uysal, M. and Assaf, A.G., 2021. A thematic analysis of crisis management in tourism: A theoretical perspective. Tourism Management, 86, p.104342.
Bhaduri, R.M., 2019. Leveraging culture and leadership in crisis management. European Journal of Training and Development, 43(5/6), pp.554-569.
Bissoondeeal, R.K., Binner, J.M. and Milas, C., 2023. Brexit and coronavirus: financial perspectives and future prospects. The European Journal of Finance, pp.1-10.
Building.co.uk, 2023. Covid sends Morgan Sindall to worst set of results since 2015. [Online]. Available at: https://www.building.co.uk/news/covid-sends-morgan-sindall-to-worst-set-of-results-since-2015/5107372.article [Accessed on 08-09-2023]
Constructionnews.co.uk, 2023. Morgan Sindall limits inflation impact amid supply chain challenges. [Online]. Available at: https://www.constructionnews.co.uk/financial/morgan-sindall-limits-inflation-amid-supply-chain-challenges-05-05-2022/ [Accessed on 08-09-2023]
Elmarzouky, M., Albitar, K. and Hussainey, K., 2021. Covid-19 and performance disclosure: does governance matter?. International Journal of Accounting & Information Management, 29(5), pp.776-792.
Gupta, R., Hasan, M.M., Islam, S.Z., Yasmin, T. and Uddin, J., 2023. Evaluating the Brexit and COVID-19’s influence on the UK economy: A data analysis. Plos one, 18(6), p.e0287342.
Gupta, R., Hasan, M.M., Islam, S.Z., Yasmin, T., Uddin, J. and Shahzad, U., 2023. Evaluating the Brexit and COVID-19’s influence on the UK economy.
Hassankhani, M., Alidadi, M., Sharifi, A. and Azhdari, A., 2021. Smart city and crisis management: Lessons for the COVID-19 pandemic. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 18(15), p.7736.
Hutahayan, B., 2020. The mediating role of human capital and management accounting information system in the relationship between innovation strategy and internal process performance and the impact on corporate financial performance. Benchmarking: An International Journal, 27(4), pp.1289-1318.
Malik, A., Adekoya, O.D., Ajonbadi, H.A. and Jimoh, I., 2019. Investigating the Potential Economic Impact of Brexit Decisions on Business Performance in the United Kingdom: A Case Study of the UK Construction Industry. International Journal of Management, Accounting & Economics, 6(4).
McCann, P., Ortega-Argilés, R., Sevinc, D. and Cepeda-Zorrilla, M., 2023. Rebalancing UK regional and industrial policy post-Brexit and post-Covid-19: Lessons learned and priorities for the future. Regional Studies, 57(6), pp.1113-1125.
McDermott, A.M., Conway, E., Cafferkey, K., Bosak, J. and Flood, P.C., 2019. Performance management in context: formative cross-functional performance monitoring for improvement and the mediating role of relational coordination in hospitals. The International Journal of Human Resource Management, 30(3), pp.436-456.
Morgan Sindall, 2023. Morgan Sindall Group | Home. [Online]. Available at: https://www.morgansindall.com/ [Accessed on 08-09-2023]
Oyegoke, A.S., Fisher, B.W., Ajayi, S., Omotayo, T.S. and Ewuga, D., 2023. The disruptive factors and longevity effects of Covid-19 and Brexit on the SMEs construction supply chain in the UK. Journal of Financial Management of Property and Construction.
Pugna, I.B., Duțescu, A. and Stănilă, O.G., 2019. Corporate attitudes towards big data and its impact on performance management: A qualitative study. Sustainability, 11(3), p.684.
Rakha, A., Hettiarachchi, H., Rady, D., Gaber, M.M., Rakha, E. and Abdelsamea, M.M., 2021. Predicting the economic impact of the COVID-19 pandemic in the United Kingdom using time-series mining. Economies, 9(4), p.137.
Richards, G., Yeoh, W., Chong, A.Y.L. and Popovič, A., 2019. Business intelligence effectiveness and corporate performance management: an empirical analysis. Journal of Computer Information Systems, 59(2), pp.188-196.
Shet, S.V., Patil, S.V. and Chandawarkar, M.R., 2019. Competency based superior performance and organizational effectiveness. International Journal of Productivity and Performance Management, 68(4), pp.753-773.
Statista, 2023. Forecast of the construction market revenue in United Kingdom from 2012 to 2027, by segment. [Online]. Available at: https://www.statista.com/forecasts/1328878/construction-market-revenue-united-kingdom [Accessed on 08-09-2023]
Stride, M., Renukappa, S., Suresh, S. and Egbu, C., 2023. The effects of COVID-19 pandemic on the UK construction industry and the process of future-proofing business. Construction Innovation, 23(1), pp.105-128.
The Guardian, 2023. Brexit: UK construction costs ‘have risen much more steeply than EU’. [Online]. Available at: https://www.theguardian.com/politics/2023/jan/24/brexit-uk-construction-costs-eu#:~:text=Analysis%20of%20data%20from%20EU,and%20steel%20increased%20by%2060%25. [Accessed on 08-09-2023]
Walsh, D., Pajón, L., Lawson, K., Hafeez, K., Heath, M. and Court, N., 2022. Increased Risks of Labor Exploitation in the UK following Brexit and the Covid-19 Pandemic: Perspectives of the Agri-food and Construction Sectors. Journal of Human Trafficking, pp.1-16.
